Computed Tomography (CT)
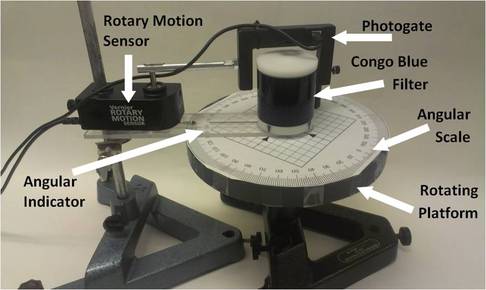
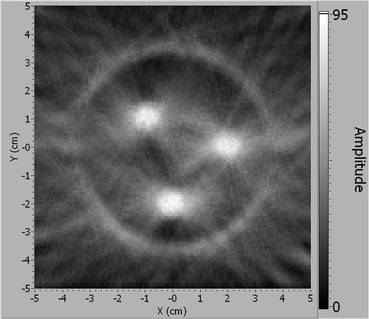
For this laboratory exercise, the instructor and students use standard physics laboratory equipment such as a photogate, a rotation sensor, and a rotation table to explore how an image is formed in Computed Tomography. Objects are placed in an enclosure made with a light filter that is largely opaque in the visible spectrum but mostly transparent to the near IR light of the photogate (880nm.) The enclosure is scanned with the photogate and an image of the contents is formed. This experiment effectively conveys how an image is formed during a CT scan and highlights the important physical and imaging concepts behind CT such as electromagnetic radiation, the interaction of light and matter, image artifacts, and windowing.
Learning Goals
Computed Tomography Learning Goals
Lab instructions
Computed Tomography Laboratory Guide (pdf) (docx)
Assessments
Resources
CT Program (executable version)
Published
Elliot Mylott, Justin C. Dunlap, Ryan Klepetka, Ralf Widenhorn , "An easily assembled laboratory exercise in computed tomography", 2011 Eur. J. Phys. 32 1227
Awards
3rd Place Winner of the "What can you teach in LabVIEW Contest" (2011).
Ralf Widenhorn, Justin C. Dunlap, Elliot Mylott, Ryan Klepetka.
1st Place Winner of the American Association of Medical Colleges (AAMC) iCollaborative Call for Physics Teaching Resources for Pre-health Competencies (January 2013)
Elliot Mylott, Ryan Klepteka, G.R. Van Ness, and Ralf Widenhorn.
https://www.mededportal.org/icollaborative/resource/645
Links