Organic Chemistry III
Dr. Carl C. Wamser
Listed below are the ConcepTests used in class, in the order they appeared. New questions and references to other related questions will be added as they become available. Boldface indicates the correct answer. Numbers indicate an estimate of your responses.
ConcepTests for Chapters 1-9 are with the Chem 334 web pages.
ConcepTests for Chapters 10-18 are with the Chem 335 web pages.
1. This is third-term organic chemistry. When did you take the second term (Chem 335 or equivalent)?
A last term with you, Dr. Wamser
B last term, somewhere else
C last year, including summer
D longer ago than one year
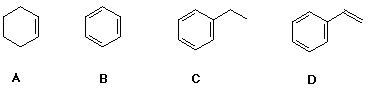
2. Which of the compounds below would be expected to react the most rapidly with a typical electrophile like Br2 ?
Challenge problem:
An old method for determining whether a disubstituted benzene was ortho, meta, or para was to perform a nitration and count the number of different mononitration products that could be isolated.
a) Apply this to the three dichlorobenzenes and indicate how the method could distinguish them.
b) Does the method work with bromochlorobenzenes?
c) Does the method work with chloronitrobenzenes?
d) This method does involve an assumption about nitration reactions and substituent effects. What is it?
3. Predict the characteristics of -NH3+ as a substituent.
A activating, o/p directing
B activating, m-directing
C deactivating, o/p directing
D deactivating, m-directing
4. Predict the characteristics of -CN as a substituent.
A activating, o/p directing
B activating, m-directing
C deactivating, o/p directing
D deactivating, m-directing
5. Predict the characteristics of -OCH2CH3 as a substituent.
A activating, o/p directing
B activating, m-directing
C deactivating, o/p directing
D deactivating, m-directing
6. To prepare m-chloronitrobenzene from benzene, one should
A first nitrate, then chlorinate
B first chlorinate, then nitrate
7. The preferred position for nitration of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
8. The major product from the Friedel-Crafts reaction of 1-bromobutane
with AlBr3 and benzene is likely to be
A bromobenzene
B butylbenzene
C sec-butylbenzene
D tert-butylbenzene
9. Which of the following will react most rapidly in a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
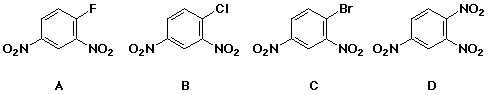
10. A mixture of (a) triethylamine, (b) benzoic acid, and (c)
butylbenzene is dissolved in diethyl ether.
The ether solution is shaken with aqueous HCl, then separated,
and the aqueous solution is saved in flask 1.
The ether solution is next shaken with aqueous NaOH, then separated,
and that aqueous solution is saved in flask 2.
The ether solution is saved in flask 3.
The original three compounds are now located in flasks 1, 2, and 3. Who's where?
A 1 (a) , 2 (b) , 3 (c)
B 1 (a) , 2 (c) , 3 (b)
C 1 (b) , 2 (a) , 3 (c)
D 1 (b) , 2 (c) , 3 (a)
11. In order to maximize the yield of butyl amine, the reaction of bromobutane with ammonia should be carried out
A with excess bromobutane
B with excess ammonia
C by slow addition of ammonia
D at low temperature
12. A reaction sequence that would convert benzene into fluorobenzene would likely involve all of the following EXCEPT
A benzenediazonium ion
B nitrobenzene
C aniline
D phenol
13. Repeated cycles of exhaustive methylation and Hofmann elimination on the amine below will eventually give a product with no nitrogen and the formula
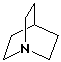
A C7 H10
B C7 H12
C C6 H10
D C4 H8
14. The pi MOs of a typical diene and an alkene are shown below. The Diels-Alder reaction works best with electron-deficient alkenes because this improves the bonding interaction between MOs
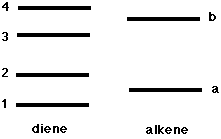
A 1 and a
B 2 and a
C 3 and a
D 2 and b
15. 2. In some cases, a Diels-Alder reaction occurs when the diene is electron-deficient and the alkene is electron-rich, in which case the bonding interaction is improved between MOs

A 2 and a
B 3 and a
C 2 and b
D 3 and b
16. The product of the Cope rearrangement of the compound below will be a
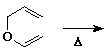
A ketone
B aldehyde
C ether
D enol
17. Pure alpha-D-glucopyranose has [a] = +112° .
Pure beta-D-glucopyranose has [a] = +19° .
After mutarotation equilibrium, [a] =
A some negative value or zero
B between 0° and +19°
C the average of +19° and +112°
D some other value between +19° and +112°
The exact average value is 65.5°. The observed rotation should be
A higher than 65.5°
B lower than 65.5°
18. Fructose exists to a significant degree as a pyranose, in which C-6 and C-2 are joined in a hemiketal linkage.
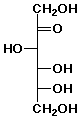
Assume the anomeric carbon 'a' has a beta OH group.
What's the other substituent on carbon 'a' ?Is the OH group on carbon 'b' up or down ?
axial or equatorial ?Is the OH group on carbon 'c' up or down ?
axial or equatorial ?Is the OH group on carbon 'd' up or down ?
axial or equatorial ?Is the OH group on carbon 'e' up or down ?
axial or equatorial ?Is this the most stable conformation?
19. The complete periodate cleavage of glucose would give
A 5 HCOOH + 1 H2CO
B 5 H2CO + 1 HCOOH
C 1 CO2 + 1 H2CO + 4 HCOOH
D 1 CO2 + 1 HCOOH + 4 H2CO
20. Compared to glucose, the complete periodate cleavage of fructose would give
A the same fragments
B 1 CO2 instead of a HCOOH
C 1 extra H2CO instead of a HCOOH
D both B & C
21. When mevalonic acid is biosynthesized from acetyl-CoA, the methyl groups of acetyl-CoA are most likely found in mevalonic acid as carbons
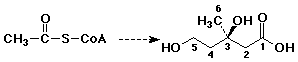
A 2, 4, 5, 6
B 2, 4, 6
C 2, 5, 6
D 2, 6
22. The unusual alkyne functional group in norethindrone is probably introduced synthetically by
A addition to a ketone
B oxidation of an alkene
C elimination from a dibromide
D epoxide ring opening
23. The pKa values for phosphoric acid are about 2, 7, and 12. At pH ~ 7, the average charge on phosphoric acid would be expected to be
A about 0
B between 0 and 1
C about 1
D between 1 and 2
24. The pKa values for phosphoric acid are about 2, 7, and 12. At pH ~ 7, the average charge on a phosphate monoester would be expected to be
A about 0
B between 0 and 1
C about 1
D between 1 and 2
25. The pKa values for phosphoric acid are about 2, 7, and 12. At pH ~ 7, the average charge on a phosphate diester would be expected to be
A about 0
B between 0 and 1
C about 1
D between 1 and 2
26. The pKa values for phosphoric acid are about 2, 7, and 12. At pH ~ 7, the average charge on a phosphate triester would be expected to be
A about 0
B between 0 and 1
C about 1
D between 1 and 2
27. The pKa values for phosphoric acid are about 2, 7, and 12. At pH ~ 7, the average charge on ATP would be expected to be
A about 1
B about 2
C about 3
D over 3
28. The expected charge on valine at pH 7 is approximately
A -1
B neutral
C +1
29. The expected charge on valine at pH 1 is
A negative
B neutral
C positive
30. The expected charge on valine at pH 10 is
A negative
B neutral
C positive
31. Given pKa values of about 2.3 and 9.7 for valine, the expected charge on valine at pH 7 is slightly
A negative
B positive
32. Given a side-chain pKa value of about 10, the expected charge on lysine at pH 7 is about
A -1
B 0
C +1
D +2
33. At pH 7, the expected charge on the dipeptide TrpArg is about
A -1
B 0
C +1
D +2
34. The strongest H-bonding would be expected between the side chains of which pair
A Leu - Lys
B His - Phe
C Glu - Tyr
D Arg - Lys
35. Which amino acid substitution is most likely to cause a significant change in a protein's structure and/or function?
A Val to Leu
B His to Trp
C Arg to Lys
D Glu to Asp
Challenge problem: Nitrite (NO2-) or nitrous acid (HONO) can act as a mutagen, in that it converts C to U.
a) Show how this reaction might occur.
b) Illustrate two cases where a C to U mutation would NOT affect
protein synthesis.
c) Identify the case where such a mutation could cause the MOST
drastic change.