Listed below are the ConcepTests used in class, in the order they appeared. New questions and references to other related questions will be added as they become available. Boldface indicates the correct answer.
These ConcepTests cover Chapters 10-19 in the Brown & Foote text.
ConcepTests for Chapters 1-9 are with the Chem 334 web pages.
ConcepTests for Chapters 20-28 are with the Chem 336 web pages.
Chapter 10 - Alkynes
64. The correct name is:
![]()
A 1-bromo-3-pentyne
B 5-bromo-2-pentyne
65. The correct name is:
![]()
A 2-methylhex-2-en-5-yne
B 5-methylhex-4-en-1-yne
66. The correct name is:
![]()
A hept-2-en-5-yne
B hept-5-en-2-yne
What else does the above name need?
cis or Z
67. Based on the location of alkynes in the table of acidities (Appendix A2), which of the following bases would be strong enough to create an acetylide anion from an alkyne?
A NH3
B CH2=CH2
C NaOH
D CH3Li
68. The correct name is
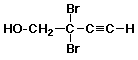
A 2,2-dibromobut-3-ynol
B 2,2-dibromobut-3-yn-1-ol
C 3,3-dibromobut-1-yn-4-ol
D something else
69. What product(s) would be expected from treatment of 1,2,3,4-tetrabromobutane with excess NaNH2 in liquid ammonia?
A 1,3-butadiyne
B 1,2,3-butatriene
C a mixture of both
D neither
70. How many equivalents of NaNH2 are used in making the diyne product in the above reaction?
A 2
B 4
C 6
D some other number
71. In a synthesis of 3-hexyne, a likely compound that could be the immediate precursor to 3-hexyne is
A 1-butyne
B 1-hexyne
C cis-3-hexene
D cis-3,4-dibromo-3-hexene
72. In a synthesis of 1-butyne, the most likely immediate precursor to 1-butyne is
A 1-propyne
B 2-butyne
C 1,2-dibromobutane
D bromoethane
Chapter 11 - Ethers
73. 1. Tert-butyl methyl ether is cleaved by dilute HCl
while most other ethers require concentrated HBr or HI.
Which of the following is NOT a possible product from
cleavage of t-butyl methyl ether by dilute HCl ?
A (CH3)3CCl
B (CH3)2C=CH2
C (CH3)3COH
D CH3Cl
74. Tert-butyl ethers are very easily cleaved by acid
because this intermediate is particularly favorable: B
75. Epoxides are highly reactive compared to most ethers
because of
A high electron density
B ring strain
C steric hindrance
D high nucleophilicity
76. Acid catalyzes epoxide ring openings because it
A increases electron density
B increases nucleophilicity
C increases ring strain
D increases leaving group ability
Chapter 12 - Mass Spectrometry
77. If the two Br isotopes, Br-79 and Br-81, each has a natural
abundance of about 50%,
what is the most likely molecular weight of Br2 ?
A 158 amu
B 160 amu
C 162 amu
D all three are equally likely
Chapter 13 - NMR
78. A magnetic nucleus with a spin quantum
number of 1 has how many spin state possibilities?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D more than 3
79. The proton NMR spectrum of isobutane consists of
how many absorptions ?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D more than 3
80. The two peaks in the proton NMR spectrum
of isobutane are in what intensity ratio ?
A 1:1
B 2:1
C 3:1
D some other ratio
81. The peak corresponding to the 3° H
in the proton NMR spectrum of isobutane
is split into what pattern ?
A singlet
B doublet
C triplet
D a larger multiplet
82. The peak corresponding to the 1° Hs
in the proton NMR spectrum of isobutane
is split into what pattern ?
A singlet
B doublet
C triplet
D a larger multiplet
Chapter 14 - IR & UV
Chapter 15 - Aldehydes & Ketones
83. The suffix for the IUPAC name for the
compound below would be
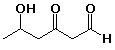
A -ol
B -one
C -al
D -onal
84. The most basic site on an aldehyde is
A C
B O
C H
D the pi bond
85. The compound expected to have the
highest boiling point is C
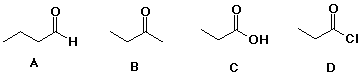
86. Which of the following is a hydrate ? C
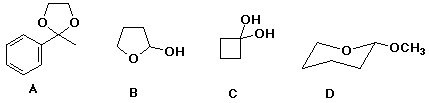
87. Which of the above is
an acetal D
a ketal A
a hemiacetal B
88. Challenge problem: group work (3 - 4 people)
Using only ethylene as a source of carbon, show how to prepare 3-hexanol using Grignard reactions.
Besides using all correct reactions, syntheses are judged on "style" points:
If you were actually carrying out this or a similar synthesis in lab,
what criteria (beyond the number of steps and the number of reagents)
would be involved in deciding whether your synthesis is a good one?
89. Which of the following is NOT likely to be in
equilibrium with acetaldehyde in aqueous acid ? B
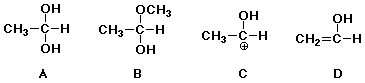
90. Which of the following is the best nucleophile ? D
Chapter 16 - Carboxylic Acids
91. At pH about 7, a typical a-aminoacid will exist in the
following form: D
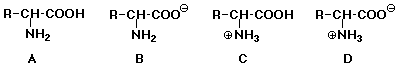
92. Because of the substituent near the carboxylic acid, an alpha-aminoacid (see above) would be expected to have a pKa
A lower than a typical carboxylic acid
B higher than a typical carboxylic acid
C the same as a typical carboxylic acid
93. Challenge problem - group work (3 - 4 people)
Refer to the table of pKa data on page 627 (#16.29).
a) Explain why the first and second pKa values for a
dicarboxylic acid are different from one another.b) Referring to the pKa of a simple alkanoic acid (pKa ~ 4.9),
describe the difference in terms of substituent effects.
(instead of charges as your Study Guide does).c) Explain why the difference is smaller for longer chains.
d) As the chain becomes longer, the limiting ratio is
Ka1 / Ka2 = 4. Why? What is the relationship to
the Ka of a simple alkanoic acid (pKa ~ 4.9) ?
Chapter 17 - Carboxyl Derivatives
94. Which is the most acidic hydrogen in this molecule? C
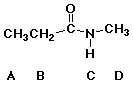
95. Which is the most acidic hydrogen in this molecule? B
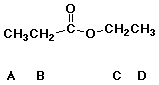
96. Hydrolysis requires only a catalytic amount of acid
for each of the following EXCEPT
A esters
B lactones
C amides
D anhydrides
97. Challenge problem: (work in small groups)
Hydrolysis of t-butyl acetate can be carried out with either
acid or base.
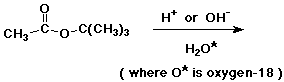
a) In O-18 enriched water, what product or products would be expected to contain O-18 ?
b) In fact, O-18 shows up in different places, depending on whether acid or base is used. Explain.
c) With acid catalysis, isobutylene (2-methylpropene) is a significant product. Where does it come from? Why isn't this seen in base?