 |
1700s Timeline
![]()
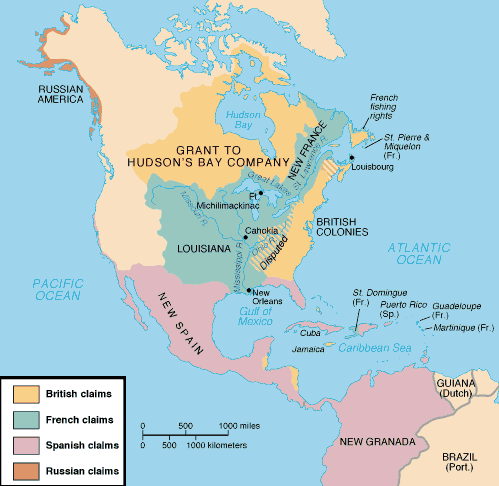
Note: The following timeline and the map above are from The American People: Creating a Nation and a Society, Gary B. Nash, et al., 2nd ed. Addison-Wesley Publishers
ALSO: This Timeline is intended to give the student a better idea of what was happening in the rest of Colonial America during the important years leading up to and immediately following the Albany Congress
| 1700s | |
| 1701 1702-1713 1704 1712 1713 .......... 1715-1730 1718 1720s 1732 1733 1734-1736 1735 1739-1740 .......... .......... 1740s 1744-1748 1747 .......... 1754 1755 1756-1763 1759 1759-1761 1760s-1770s 1760s 1760 1763 .......... .......... 1764 1765 .......... 1766 .......... 1767 1768 1769 1770 .......... 1771 1772 1773 1774 .......... 1775 .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 1776 .......... .......... .......... .......... 1777 .......... .......... .......... 1778 .......... 1779 .......... .......... 1780s .......... 1781 .......... 1783 .......... .......... 1784 .......... 1785 .......... .......... 1786 .......... 1786-1787 1787 .......... .......... 1788 1789 .......... 1790 .......... 1791 .......... .......... 1792 1793 .......... .......... 1794 1795 1796 .......... 1797 1798 .......... 1798-1800 1799 1801 |
Iroquois
set policy of neutrality Queen Anne's War Boston News-Letter, first regular colonial newspaper, published Slave revolt in New York City Peace of Utrecht Beginning of Scots-Irish and German immigration Volume of slave trade doubles French settle New Orleans Black population begins to increase naturally Georgia founded for English paupers and buffer against Florida Molasses Act Great Awakening begins in Northampton, Massachusetts Zenger acquitted of seditous libel in New York Whitefield's first American tour spreads Great Awakening Slaves compose 90% of population in Carolina rice coast Stono Rebellion in South Carolina Indigo becomes staple crop in Lower South King George's War Benjamin Franklin publishes first Poor Richard's Almanack Impressment riot in Boston Albany conference Braddock defeated by French and Indian allies Seven Years' War Wolfe defeats the French at Quebec Cherokee War against the English Spanish establish California mission system Economic slump: 1761-1765 depression his most colonies Africans compose 20% of American population Treaty of Paris ends Seven Years' War Proclamation line limits westward expansion See also Steps on the Road to Revolution Sugar and Currency Acts. Pontiac's Rebellion in Ohio Valley Colonists resist Stamp Act Virginia House of Burgesses issues Stamp Act resolutions Declaratory Act. Tenant rent war in New York Slave insurrections in South Carolina Townshend duties imposed British troops occupy Boston American Philosophical Society founded at Philadelphia "Boston Massacre" Townshend duties repealed (except on tea) North Carolina Regulators defeated Gaspee incident in Rhode Island Tea Act provokes Boston Tea Party "Intolerable Acts" First Continental Congress meets Second Continental Congress meets Battles of Lexington and Concord Lord Dunmore's proclamation to slaves and servants in Virginia Iroquois Six Nations pledge neutrality Continental Congress urges "states" to establish new governments Postal system established by Continental Congress Thomas Paine publishes Common Sense British evacuate Boston and seize New York City Declaration of Independence Eight states draft constitutions Cherokee raids and American retaliation British occupy Philadelphia Most Iroquois join the British Americans win victory at Saratoga Washington's army winters at Valley Forge War shifts to the South. Savannah falls to British French treaty of alliance and commerce Massachusetts state constitutional convention Charleston surrenders to British Pennsylvania begins gradual abolition of slavery Virginia and Maryland debate abolition of slavery Destruction of Iroquois Confederacy Cornwallis surrenders at Yorktown Articles of Confederation ratified by states Peace Treaty with England signed in Paris Massachusetts Supreme Court abolishes slavery King's Commission on America Loyalists begins work Treaty of Fort Stanwix with the Iroquois Spain closes Mississippi River to American navigation Treaty of Hopewell with the Cherokee Land Ordinance for the Northwest Territory Jay-Gardoqui negotiations Virginia adopts "Bill for Establishing Religious Freedom" Annapolis convention calls for revision of Art. of Confederation Shay's Rebellion Northwest Ordinance Constitutional Convention Federalist Papers published by Hamilton, Jay and Madison Constitution ratified George Washington inaugurated as first president Outbreak of French Revolution Slave trade outlawed in all states except Georgia and S. Carolina Hamilton's "Reports on the Public Credit" Bill of Rights ratified Whiskey tax and national bank established Hamilton's "Report on Manufactures" Washington reelected Outbreak of war in Europe Washington's Neutrality Proclamation Jefferson resigns from cabinet Whiskey Rebellion in Pennsylvania Controversy over Jay's Treaty with England Washington's Farewell Address John Adams elected president XYZ affair in France Naturalization Act; Alien and Seditions Acts Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions Undeclared naval war with France Trials of David Brown and Luther Baldwin Jefferson elected president by House of Representatives |
Home Page | Assessment
| Lesson 1 | Lesson
2 | Lesson 3 | Lesson
4 | Frontier
Characters
Learning Aids | Great
Law of Peace | US Constitution
| Timeline | Works
Cited
© 1 October 2001, Portland State University