

Chapter 11 - Condensation Reactions

Reactive Sites of the Carbonyl Group

Greek letters in nomenclature
- alpha position is the carbon that is attached to the functional group

Enols
- tautomers - constitutional isomers that are easily interconverted
enol structure vs. carbonyl (keto) structure differs by location of one
H (and double bond)

- most carbonyl and carboxyl compounds are in equilibrium with just small
amounts of enol
enol form is favored only in special cases if the C=C double bond or the
O-H group is specially stabilized

cyclohexanone (1 enol per million ketone molecules)

24% 2,4-pentanedione : 76% 4-hydroxy-3-penten-2-one
(see problem 11.21 - the extra stabilization of the enol is H-bonding)
- knowing the right keto-enol forms for the nucleic acid bases allowed
Watson and Crick to develop the double-helix concept for DNA

guanine (keto form - as in DNA) // guanine (enol form - aromatic but less
stable)
Acid- and Base-Catalyzed Enolization

Alpha-Substitution on Enols
- enols behave like C=C double bonds - react with electrophiles
the net reaction is alpha-substitution

Enolate Anions
- carbonyl compounds have pKa values about 20
see Table 11.1 to compare other families
- strong bases can deprotonate carbonyl compounds

- two carbonyl groups increases the acidity further
pKa of 1,3-diketones is about 9

- enolates are good nucleophiles
- enolates are ambident (two-toothed) nucleophiles
usually they react at the C rather than the O anion site

Alpha-Substitution on Enolate Anions
- use of enolate nucleophile in an SN2 substitution
product is an alpha-substituted carbonyl (or carboxyl) compound
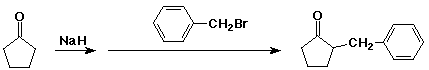
The Aldol Condensation
- reaction of an enolate as nucleophile with a carbonyl group,
usually from the same compound

- the reaction is a reversible equilibrium
favored towards product (aldol) only for simple aldehydes
greater substitution favors starting compounds at equilibrium

- the aldol reaction is often combined with dehydration of the initial
aldol product, forming a conjugated double bond (an enone)

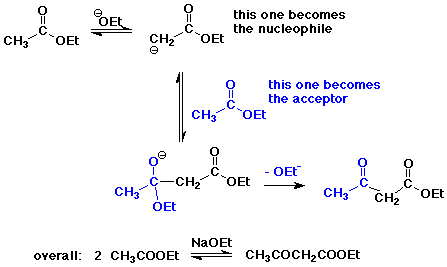
The Claisen Condensation
- condensation with a carboxyl derivative gives substitution instead
of addition
- the Claisen condensation gives beta-ketoesters
Other Related Condensation Reactions
- alpha-anions (nucleophiles) can be made next to any good electron-withdrawing
group
- these anions can react with carbonyl compounds to give addition
or with carboxyl compounds to give substitution
- acetyl coA often acts as a biological nucleophile at its alpha-position
formation of acetoacetyl coA is the first step in building up fatty acids
(Note - we will skip the malonic ester synthesis)
![]()
![]()
![]()










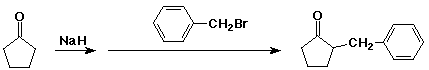


![]()
