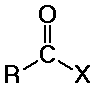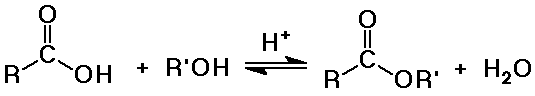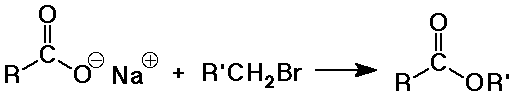Chapter 10 - Carboxyl Compounds

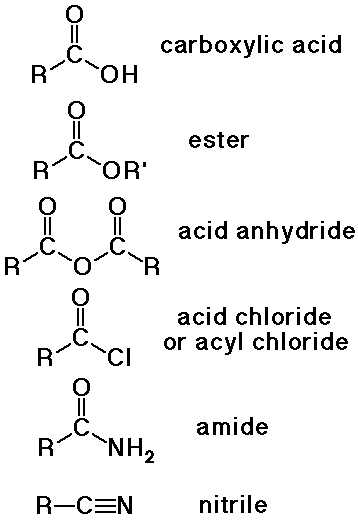
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
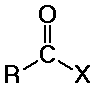
distinguished from aldehydes and ketones because one substituent is NOT
C or H
(usually Cl, O, or N, but it could also be other F, Br, I, S, P, or many
other possibilities)
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids
- alkanoic acid (-oic acid suffix)
when the -COOH is part of the parent chain
assumed #1 position
- cycloalkanecarboxylic acid
when the -COOH is not part of the parent name
assumed attached to the #1 position
- common names
formic acid (methanoic acid)
acetic acid (ethanoic acid)
notice the prefixes are the same as for aldehydes
- acyl group names
needed for naming some derivatives
formyl (methanoyl)
acetyl (ethanoyl)
Nomenclature of Carboxyl Derivatives
- acid halides
alkanoyl halide (-oyl halide suffix)
or use common acyl name from acid
- acid anhydrides
alkanoic anhydride (-oic anhydride suffix)
- amides
alkanamide (-amide suffix)
substituents on N use prefix N- (instead of a number location)
- nitriles
alkanenitrile (-nitrile suffix)
- carboxylate salts
metal alkanoate (-oate suffix for anion)
- esters
alkyl alkanoate (a two-part name)
alkyl group is attached to the O
alkanoate analogous to carboxylate salt
Nomenclature Examples
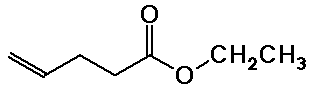
ethyl 4-pentenoate
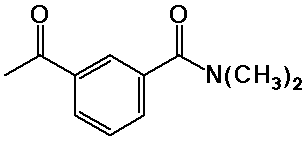
N,N-dimethyl-3-acetylbenzamide
Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids
- very polar functional group with H-bonding
typically the boiling points are relatively high
(formic acid, b.p. 100.7°)
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids
- stronger acids than alcohols
Ka ~ 10-5 (pKa ~ 5)
(alcohol pKa values about 15-18)
- electron-withdrawing effects of the carbonyl group tends to further
polarize the O-H bond so it is more easily ionized
- the carboxylate anion is stabilized by resonance
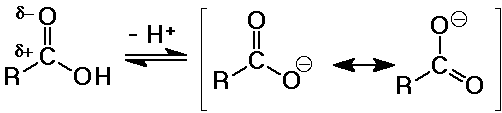
- substituent effects
electron-withdrawing groups (like Cl) increase acidity
Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids
- oxidations
alkylaromatics to benzoic acids using KMnO4
primary alcohols to carboxylic acids using CrO3
aldehydes to carboxylic acids using Tollen's reagent (Ag+)
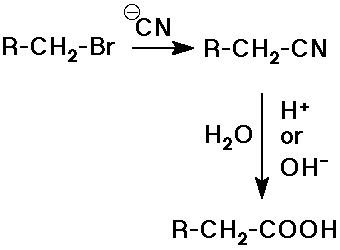
- hydrolysis of nitriles
alkyl halide to nitrile by SN2 substitution
followed by hydrolysis with acid or base catalysis
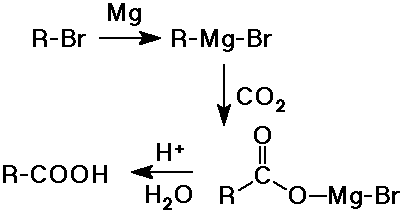
- addition of CO2 to a Grignard reagent
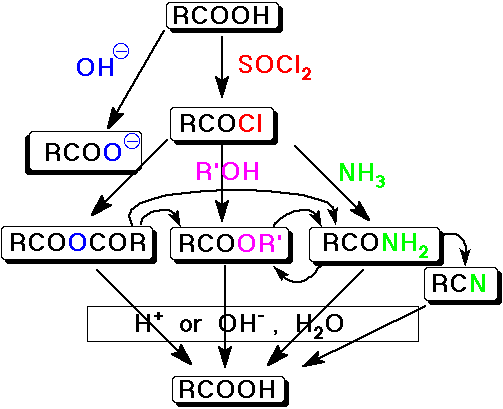
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
- the major reaction of carboxyl derivatives
- starts like nucleophilic addition, but becomes substitution when the
leaving group deoarts
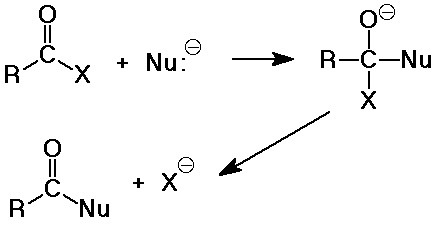
- the tetrahedral intermediate is like that in carbonyl additions
- the product is often another carboxyl derivative
(depnding on what the nucleophile is)
- compared to other nucleophilic substitutions:
SN2 - simultaneous bonding of nucleophile and loss of leaving
group
SN1 - first loss of leaving group, then bonding of nucleophile
(cation intermediate)
acyl - first bonding of nucleophile, then loss of leaving group (anion
intermediate)
Reactivity in Acyl Nucleophilic Substitution
- better leaving groups increase reactivity
acid halides > acid anhydrides > esters > amides
- the more reactive derivatives can be easily converted to the others
you can make any of them with the acid chloride - a typical starting point
for synthesis
- all the derivatives can be hydrolyzed to the carboxylic acid
(water as the nucleophile - using acid or base catalysis)
Examples of Acyl Nucleophilic Substitution

Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
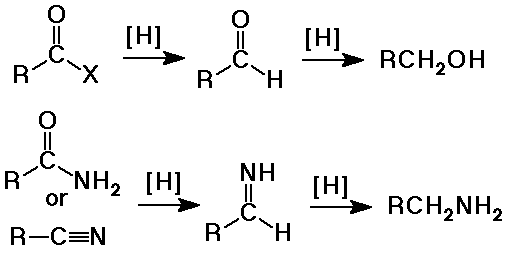
- reduction to primary alcohols by LiAlH4
- conversion to acid chlorides with SOCl2
conversion to other derivatives via the acid chloride

- conversion to esters with alcohol and acid catalysis
(Fisher esterification method)
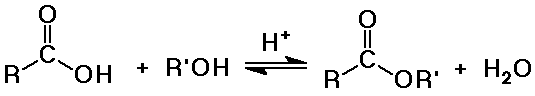
- a reversible equilibrium
favored to the right with excess alcohol
favored to the left with excess water (hydrolysis)
- complete mechanism
see your text - will also be shown on the computer
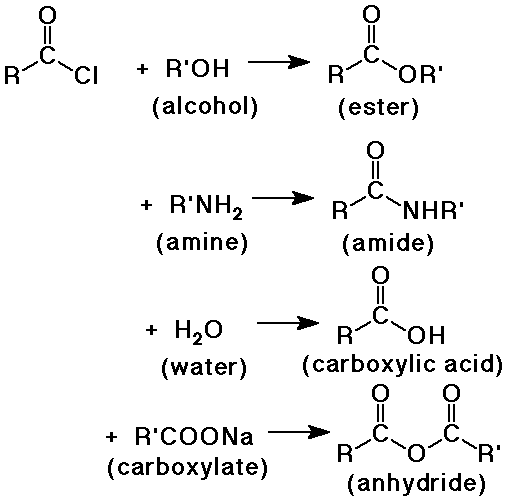
Conversion of Acid Halides into Other Carboxyl Derivatives
- acid halides are the most reactive carboxyl derivative
- they can be converted to all the other derivatives
Conversion of Acid Anhydrides into Other Carboxyl Derivatives
- acid anhydrides are the second most reactive carboxyl derivative
- they can be converted to all the other derivatives except acid halides
- but acid chlorides are typically preferred
Synthesis of Esters
- from acid halides plus alcohols
- from acids plus alcohols (Fisher esterification)
- by SN2 reaction of a carboxylate as nucleophile
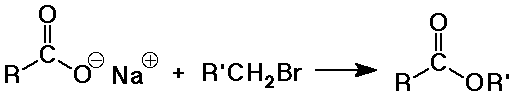
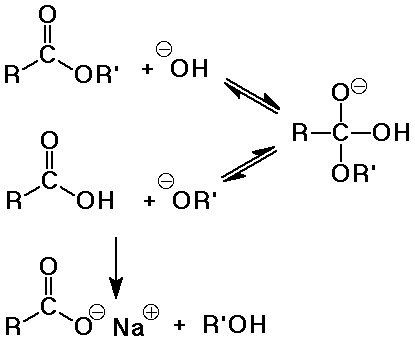
Hydrolysis of Esters
- water as the nucleophile with either acid or base catalysis
- acid-catalyzed hydrolysis is the exact reverse of Fisher esterification
(same mechanism)
- base-catalyzed hydrolysis is often called saponification (soap-making)
saponification is irreversible because a carboxylate salt is formed
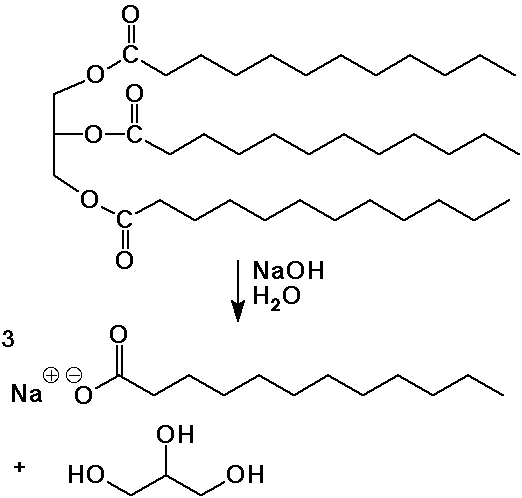
- soaps are the salts of long-chain (fatty) acids (C8 - C20)
fats are the esters of fatty acids and glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol)
Other Reactions of Esters
- reduction by LiAlH4 gives primary alcohols (plus the ester alcohol)
(H- nucleophile first gives substitution - aldehyde intermediate,
then another H- nucleophile gives addition - alcohol product)
- Grignard additions give tertiary alcohols (double addition)
(RMgX nucleophile first gives substitution - ketone intermediate,
then another RMgX nucleophile gives addition - alcohol product)
Synthesis of Amides
- acid chloride plus ammonia (or amine)
Reactions of Amides
- hydrolysis to carboxylic acid - requires prolonged heating
proteins are held together by amide bonds
- reduction by LiAlH4 to amines
Synthesis of Nitriles
- SN2 reaction of primary halides with CN-
- dehydration of amides
Reactions of Nitriles
- nucleophilc additions similar to carbonyl group (polar triple bond)
- hydrolysis to carboxylic acids
- reduction with LiAlH4 to amines
- addition of Grignards to make ketones
Polymers of Esters and Amides
- step-growth polymers are made by multiple reactions of multifunctional
monomers
- a dicarboxylic acid reacts with a diamine to form a polyamide (nylon)
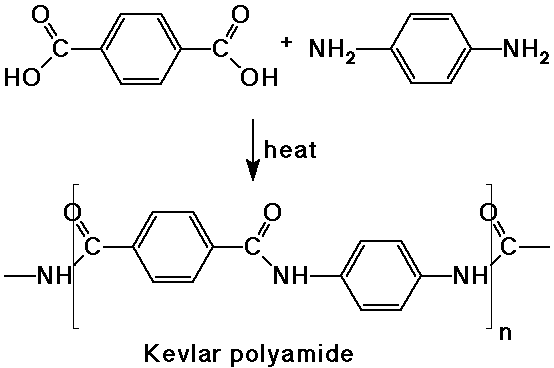
- polyesters are made from dicarboxylic acids and dialcohols
- step-reaction polymerization is a fundamentally different way to make
polymers from chain-reaction polymerization
- chain-reaction: a few reactive sites grow long chains quickly
- step-reaction: reaction steps slowly grow larger and larger chains
- interfacial polymerization - method of making thin films of polymers
as in artificial photosynthesis
Thiol Esters
- Nature often uses sulfur groups as excellent nucleophiles (and leaving
groups)
- coenzyme A contains a thiol group (coA-S-H)
- acetyl CoA acts like acetyl chloride
e.g., acetyl CoA + amines gives acetamides
Summary - Interconversion of Carboxyl Derivatives
Summary - Hydride Reductions
Summary - Grignard Reactions

![]()
![]()
![]()