![]()
![]()
![]()
McMurry, pp 320-324:
Problems 10.31-34, 36-41, 44, 46, 49, 53, 54, 57, 61
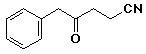
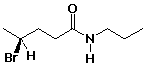
c) 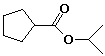
2. A typical protein linkage is an amide bond (also called a peptide
bond), such as might be found in N-methylacetamide. Proteins are typically
hydrolyzed in strong acid. Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed
hydrolysis of N-methylacetamide.
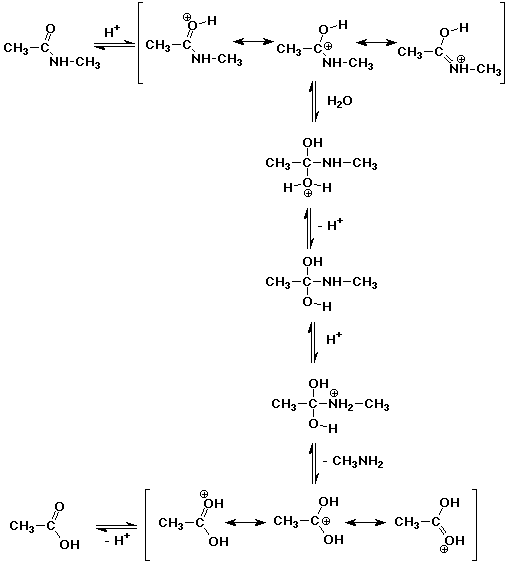
3. A typical fat has ester functional groups (most typically it is
a triester between three fatty acids and glycerol). Glycerol is 1,2,3-propanetriol,
and a fatty acid might be decanoic acid. Write the structure for the triester
made from these components.

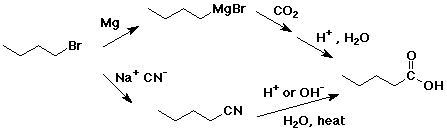
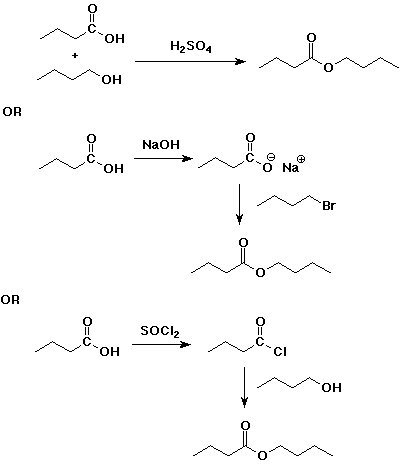
4. Using butanoic acid as the only organic starting material, show
how to prepare:
a) 1-butanol
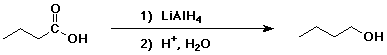
b) 1-bromobutane
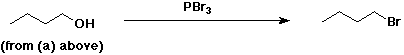
c) butyl butanoate
d) butanamide
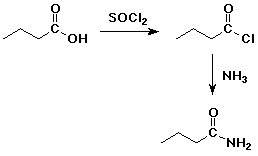
e) pentanoic acid