![]()
![]()
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete structures for the following:
a) the dipeptide ValGln as it would appear at pH 7
b) ATP (adenosine 5'-triphosphate)
c) glyceryl triacetate
2. (15 points)
a) If a sample of DNA is analyzed and found to contain 32% A and 18% G, what must be the rest of the base composition?
b) Using just the 20 common amino acids, how many different tripeptides can be created?
c) In an electrophoresis experiment, which of the 20 common amino acids would migrate towards the anode (the negative electrode) at pH 9 ?
3. (15 points) The name for the amino acid threonine comes from its similarity in structure to the sugar D-threose, shown below.
Write the structure for threonine in a Fischer projection that clearly shows its similarity to D-threose. Identify each stereocenter in threonine as R or S.
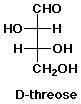
Only one other amino acid (of the 20 common ones in your table) has two stereocenters. Which one? Write its structure with both stereocenters in the S configuration.
4. (15 points) Some of the three-letter codes in the codon table can be deduced by use of simple nucleic acid polymers that are easy to make. For example, if poly-U is fed to the bacteria E. coli, an excess of the amino acid phenylalanine appears. Explain
What amino acids would be expected from poly-G, poly-C, and poly-A ?
What amino acids would be expected from a regular alternating copolymer of A and C (i.e., ACACACACACACAC ) ?
5. (15 points) Consider an unknown heptapeptide consisting of the following amino acids: Arg, Asp, His, Ile, Phe, Tyr, Val
Deduce its primary structure from the following data:
the N-terminus is Asp
the C-terminus is Phe
chymotrypsin cleaves it to a tripeptide and a tetrapeptide, A and B
A has Ile at its N-terminus and Phe at its C-terminus
B can be partially hydrolyzed to give dipeptides Arg Val, AspArg and ValTyr
Use the amino acids in this peptide to illustrate the following aspects of tertiary structure. Draw just the specific side chain structures involved.
a) ionic attraction
b) H-bonding
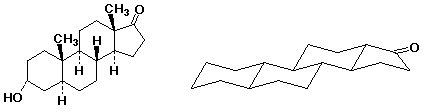
6. (10 points) The structure of the male hormone androsterone is shown below. Complete the structure on the right by properly locating each of the seven substituents that are specifically shown on the left structure. Identify each substituent as either axial or equatorial (use A or E).
7. (15 points) Glutamic acid has two carboxylic acid groups with different pKa values. The structure is shown in its fully protonated form below, with its three pKa values. Referring to the pH diagram below, write the structures of the major forms that would be expected in solution within each of the pH ranges marked A, B, C, and D.
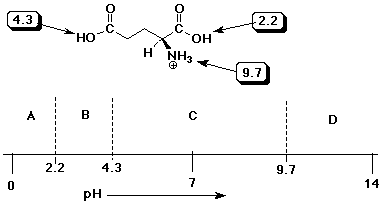
Explain why the two carboxylic acid groups have different pKa values.