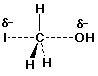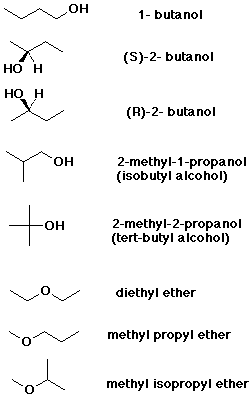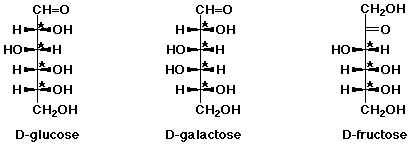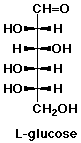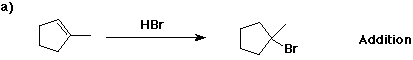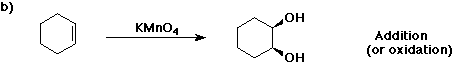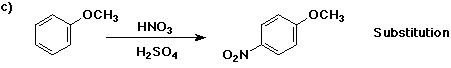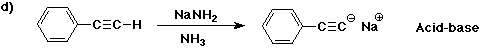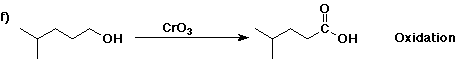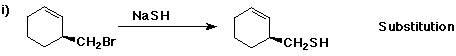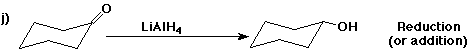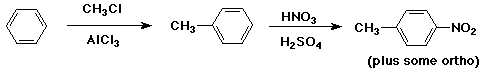Chemistry 331 - Winter 1996
Elements of Organic Chemistry I

Professor Carl C. Wamser

FINAL EXAM - Answer Key
March 19, 1996
1. (25 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including
designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown.
a) 
trans-1-isopropyl-4-methoxycyclohexane
b) 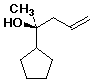
(S)-2-cyclopentyl-4-penten-2-ol
c) 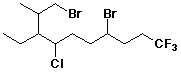
4,10-dibromo-7-chloro-8-ethyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-9-methyldecane
d) 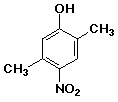
2,5-dimethyl-4-nitrophenol
e) 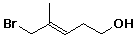
(E)-5-bromo-4-methyl-3-penten-1-ol
2. (25 points) Write accurate structures for each of the following:
a) a Newman diagram of the most stable conformation of 2-phenylethanol
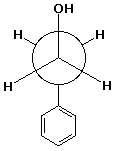
b) the transition state for SN2 reaction of methyl iodide
with hydroxide ion
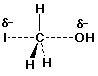
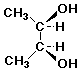
c) meso-2,3-butanediol
d) lithium isopropoxide
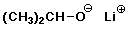
e) (E)-3,5-dimethyl-3-heptene
3. (15 points) Draw and name all the isomers that have the molecular
formula C4H10O.
Just one isomer is chiral. Draw and identify both the R and S enantiomers.
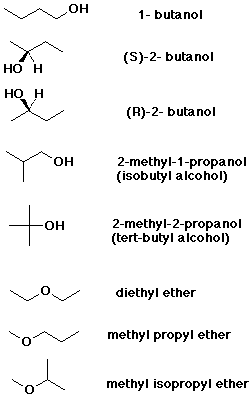
4. (10 points) The structure of several common sugars are shown below.
All have the molecular formula C6H12O6.
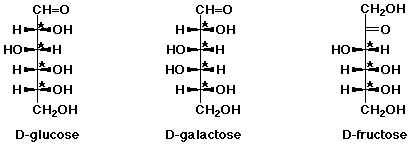
Identify each stereocenter on the three compounds above with asterisks (*).
Identify the relationship between each pair of compounds:
(either constitutional isomers, diastereomers, enantiomers, or other)
D-glucose and D-galactose are -- diastereomers
D-glucose and D-fructose are -- constitutional isomers
D-galactose and D-fructose are -- constitutional isomers
The enantiomer of D-glucose (L-glucose) does not occur naturally.
Write its structure.
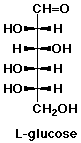
5. (10 points) Explain why fats are typically water-insoluble, while
sugars are typically water-soluble. See the previous page for the structure
of typical sugars. A typical fat has the structure shown below.

Sugars have lots of polar O-H groups, which can hydrogen-bond with water.
Fats are mainly C-C and C-H bonds, which are nonpolar and do not interact
well with water.
6. (40 points) Complete each reaction by adding the missing part: either
the major product or the necessary reagents and conditions.
Also indicate the reaction type for every reaction:
(either addition, elimination, substitution, oxidation, reduction, acid/base,
or other)
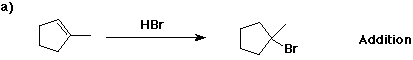
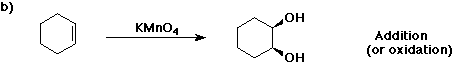
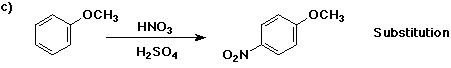
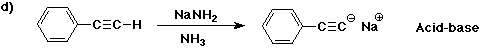
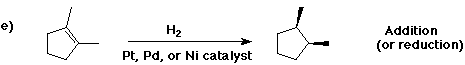
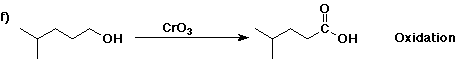
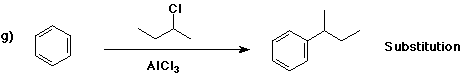
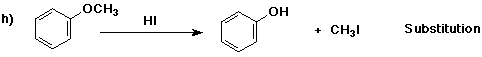
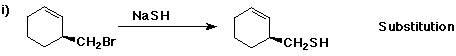
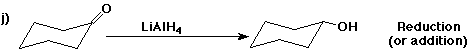
7. (15 points) The general structure of a steroid is shown below, in
two different views.
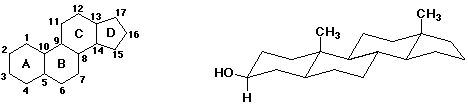
Consider the B ring as a pair of substituents on the A ring. Are they
cis or trans?
trans
Consider the A ring as a pair of substituents on the B ring. Are they cis
or trans?
(Hint: you should get the same answer for both of the above questions)
trans
Is the B - C ring connection cis or trans?
trans
Is the C - D ring connection cis or trans?
trans
A typical steroid has what are often called "angular" methyls:
axial methyl groups at positions C-10 and C-13. Draw them on the chair structures
at the appropriate places.
Cholesterol also has an equatorial alcohol group at position 3. Draw it
on the chair structure at the appropriate place, and indicate whether the
stereochemistry is R or S.
S
8. (10 points) Write a complete mechanism for the E1 dehydration of
tert-butyl alcohol using aqueous sulfuric acid.

9. (10 points) Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed ring
opening of ethylene oxide (epoxyethane) in aqueous sulfuric acid.

10. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the bromination of benzene
using FeBr3 as catalyst.
Include a potential energy diagram that identifies the steps in the reaction.
Write all resonance forms for the intermediate involved.
Illustrate why FeBr3 is considered a catalyst for this reaction.
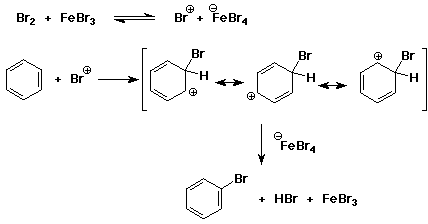
Note that FeBr3 recycles and can be used again (i.e., it
is a catalyst).
The potential energy diagram should show the addition of Br+ as endothermic
(uphill) and the regeneration of the aromatic ring as exothermic (downhill).
11. (20 points) In designing a synthesis, it is often crucial to
do things in the right order. In the two examples below, describe the strategy
necessary and show the reactions that would be used for a successful synthesis.
a) In the synthesis of p-nitrotoluene from benzene, explain how you would
choose which of the two substituents should be added first.
The methyl group should be added first, because it is ortho,para-directing.
If the nitro group were added first, it would be meta-directing, and furthermore
would be so deactivating that the Friedel-Crafts reaction would probably
not work.
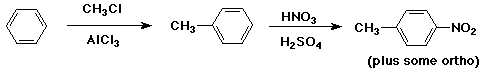
b) In the synthesis of ethyl isopropyl ether, explain how you would
select which component should be the nucleophile and which should be the
alkyl halide for the SN2 reaction.
The isopropoxide should be selected as the nucleophile and the ethyl
group as the halide, because the primary alkyl halide (ethyl) is more likely
to undergo the SN2 reaction well. The reverse pair of compounds (ethoxide
plus 2-propyl halide) is more likely to lead to E2 elimination.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()