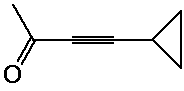Chemistry 331 - Winter 1996
Elements of Organic Chemistry I

Professor Carl C. Wamser

EXAM 1
February 6, 1996
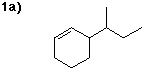
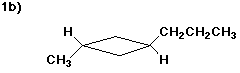
1. (12 points) Write a complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds,
including designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:

2. (20 points) Write accurate structures for each of the following names:
a) isobutylcyclobutane
b) cis-1-bromo-3-methylcyclopentane
c) the chair structure for the most stable conformer of tert-butylcyclohexane
d) a Newman diagram for the most stable conformer of 1-bromopropane
e) (Z)-4,6-dimethyl-3-heptene
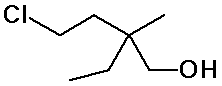
3. (10 points) For the compound shown below:
Write the molecular formula (i.e., CxHy.... ).
Identify each carbon atom as 1°, 2°, 3°, or 4°.
4. (10 points) For the compound shown below:
Write the molecular formula.
Identify the expected hybridization of each carbon atom.
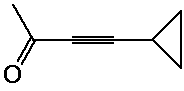
5. (15 points) Predict whether the following reactions would be expected
to have a more favorable equilibrium to the right or to the left.
a) CH3OH + NaNH2 <====> CH3ONa + NH3
pKa = 16 pKa = 33
b) CH3OH + HI <====> CH3I + H2O
delta H = - 13 kcal/mole
Ea = 15 kcal/mole
Write as much as you can of a potential energy diagram for the second
reaction.
Clearly label what the x and y axes represent, the location of the reactants
and the products, and where delta H and Ea would be measured.
Explain what additional information would be needed to make it complete.
6. (15 points) The structures shown below are meant to be the two chair
conformations of the same compound. Properly locate the two missing substituents
on the conformation on the right.
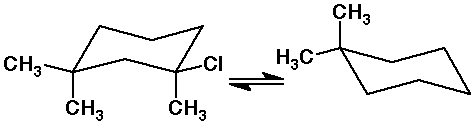
If delta H = - 1.3 kcal/mole for the equilibrium as shown, explain what
information this tells you about the relative interactions between methyl
and chloro substituents.
7. (18 points) Rewrite each of the reactions shown below, providing more
detailed structures that clearly show the following:
Identify the bonds that are broken.
Identify the new bonds that are made.
Identify which reactant acted as a nucleophile and which as an electrophile.
CH2=O + CH3Li -----> CH3CH2O- Li+
CH3NH2 + CH3I -----> (CH3)2NH2+ I-
Select either of the two reactions and explain why the reactants have
the properties of a nucleophile or electrophile.
![]()
![]()
![]()