![]()
![]()
![]()
1. (25 points) Write a complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds, including designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 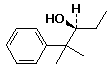
b) 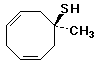
c) ![]()
d) 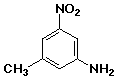
e) 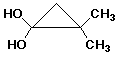
2. (18 points) Identify the relationship between the following pairs of molecules as one of the following:
A - identical structures
B - constitutional isomers
C - conformational isomers
D - diastereomers
E - enantiomers
F - resonance structures
G - none of the above

3. (6 points) Indicate the appropriate degree of hybridization for the carbon atoms in each of the structures below, selecting from the following: a = non-hybridized; b = sp hybridized; c = sp2 hybridized; d = sp3 hybridized.
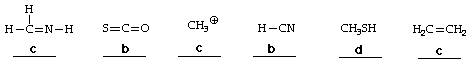
4. (6 points) Refer to the reaction below:
![]()
a) if the starting material is the S enantiomer, the product will be (circle one):
R / S / racemic / can't tell / other
b) if the starting material has () optical rotation, the product will necessarily be (circle one):
(+) / () / (+,) / can't tell / other
5. (4 points) Arrange the following in order of increasing Bronsted basicity (weakest first):
1. OH 2. Cl 3. H2O 4. NH3
a) 2 < 3 < 4 <1 b) 3 < 4 < 2 < 1 c) 4 < 1 < 2 < 3 d) 3 < 4 < 1 < 2
6. (4 points) Indicate which structure represents the most stable conformation of cis-1,4-cyclohexanediol (circle one):
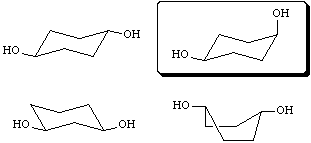 none of these
none of these
7. (20 points) Write clear structures for the following:
a) a Newman diagram of the anti conformation of 1-bromopropane
b) a Fischer projection of meso-2,3-butanediol
c) the best resonance form for the conjugate base of phenol
d) benzyl isobutyl ether
e) (Z)-1-phenyl-1,3-butadiene
8. (30 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Indicate stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 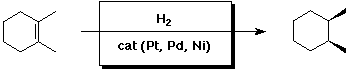
b) 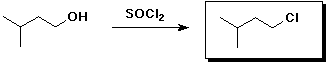
c) 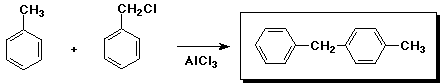
d) 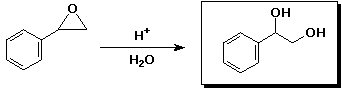
e) 
f) 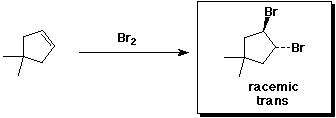
g) 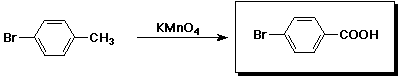
h) 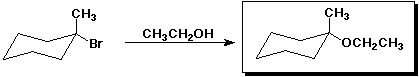
i) 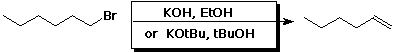
j) 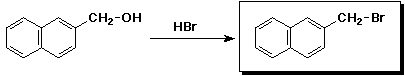
9. (20 points) The general structure of a steroid ring system is shown below, in both a top view and a side view.
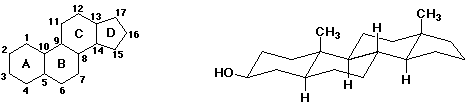
The A and B rings are said to be "fused". The B ring is like two substituents on the A ring, and vice versa. Is the A/B ring connection cis or trans?
trans
"Angular" methyl groups are frequently at positions 10 and 13. Place them on the structure on the right and indicate if each is axial or equatorial.
both are axial
Many steroids have an equatorial OH group at position 3. Place it on the structure on the right and indicate whether it is (R) or (S).
(S)
The "bridgehead" positions are the tertiary carbons at the junctures of two rings. Place hydrogens accurately on the remaining bridgehead positions.
What is the molecular formula of the steroid you have created ? (including the extra methyls and the OH)
C19 H32 O
10. (20 points) You are attempting to determine if the hydrolysis reaction of an alkyl bromide (R-Br + H2O) follows an SN1 or SN2 mechanism. Explain how you would interpret the following observations:
a) R-Br doesn't react as fast as R-I under comparable conditions.
b) You add NaCN (a good nucleophile) to the reaction and find some R-CN product has formed, but the rate of disappearance of R-Br is still the same as without the NaCN present.
c) You add some NaBr and the rate of disappearance of R-Br decreases.
d) Describe another experiment you might do to help determine the mechanism.
11. (22 points) The reaction shown below is fully reversible, which means that the mechanism written in the forward direction is completely applicable to the reaction in the reverse direction as well. Write the complete mechanism, showing all steps and electron-pushing arrows for each step.
Write an approximate potential energy diagram (assume delta H = 0) and predict the rate-determining step for the forward reaction and also for the reverse reaction.
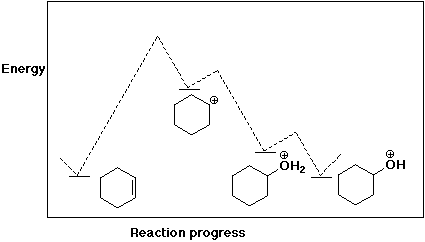
12. (25 points) Write a complete mechanism for the Friedel-Crafts methylation of bromobenzene using AlCl3 as catalyst. Just show the pathway to the formation of p-bromotoluene. Show all steps and write all resonance forms for any intermediates involved. Explain why bromo is an ortho,para-directing substituent by referring to your mechanism.