
Portland State University - - Professor Carl C. Wamser

Chapter 3 Notes - Alkenes & Alkynes

Alkenes
- C=C double bond
- Cn H2n - general formula
- unsaturated
not "saturated" with maximum hydrogens
unsaturated fats have some double bonds (easier to digest)
- note that cycloalkanes also are Cn H2n
Alkene Nomenclature
- parent alkene is the longest continuous carbon chain that includes
the double bond
- number from the end that gives the double bond the lower number
- use -ene suffix and only the first number of the double bond
- name substituents as usual
Cycloalkene Nomenclature
- double bond assumed at C1-C2
- number in the direction that gives substituents lower numbers
 3-methylcyclohexene
3-methylcyclohexene
 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene
Alkene Structure
- C=C double bond is one sigma bond and one pi bond
- sp2 hybridization (trigonal planar)
- pi bond doesn't rotate
- unlike ethane, ethene has no other conformers
Cis-Trans Isomers
- another example of stereoisomers
- 2-butene has two isomers:
 trans-2-butene
trans-2-butene
 cis-2-butene
cis-2-butene
- usually trans is more stable than cis
Cis-Trans Isomers
- an alkene can have cis-trans isomers only when each C in the double
bond is attached to 2 different groups
Stereochemistry Designation
 cis or trans ?
cis or trans ?
- note that cis-trans works only for disubstituted alkenes
- E,Z designation is more general
E,Z Designation
- assign priorities to the two groups on each C of the double bond (high,
low for each C)
- if the the two high priority groups are on the same side, it is Z
- if the the two high priority groups are on opposite sides, it is E
Sequence Rules
- assign priority based on the atoms directly attached to the carbons
of the double bond
- higher priority goes to:
- higher atomic number
- break ties by considering the next bonded atoms
Practice Nomenclature
 (E)-3,4-dimethyl-2-octene
(E)-3,4-dimethyl-2-octene
 (Z)
(Z)
Alkynes
Structure
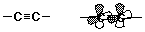
- carbon-carbon triple bond
- sp hybridization (linear)
- no cis-trans possibilities
- the two pi bonds are perpendicular
- high electron density
- (usually more reactive than alkenes)
Alkynes - Nomenclature
- -yne suffix (with number)
- rules similar to alkenes
- with both -enes and -ynes, suffix is -en-yne and numbering is from
the end closer to a multiple bond
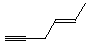
- (E)-4-hexen-1-yne
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 3-methylcyclohexene
3-methylcyclohexene![]() 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene trans-2-butene
trans-2-butene cis-2-butene
cis-2-butene cis or trans ?
cis or trans ? (E)-3,4-dimethyl-2-octene
(E)-3,4-dimethyl-2-octene (Z)
(Z)![]()