![]()
![]()
![]()
1. (25 points) Write a complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds, including designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 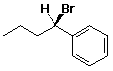
b) ![]()
c) ![]()
d) 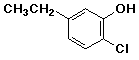
e) 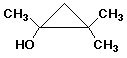
2. (18 points) Identify the relationship between the molecules in each of the following pairs. Use one of the following letter designations:
A - identical structures
B - constitutional isomers
C - conformational isomers
D - diastereomers
E - enantiomers
F - resonance forms
G - none of the above
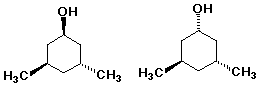 A
A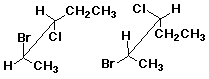 D
D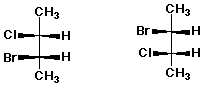 E
E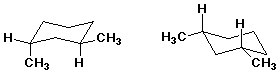 D
D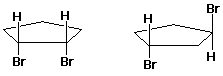 B
B3. (12 points) Identify which of the following pairs represent valid contributing resonance structures. (Circle the pair if they are valid resonance forms)
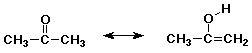 NO
NO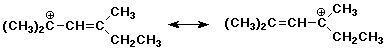 YES
YES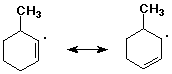 NO
NO4a. (5 points) Which of the labeled points in the reaction energy diagram below corresponds to the transition state for the rate-determining step? Circle the appropriate response.
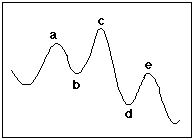 a b c d e (none of the above)
a b c d e (none of the above)C
4b. (5 points) Which structure best represents the transition state for the reaction of hydroxide ion with methyl iodide? Circle the appropriate response.
B
5. (15 points) Give the molecular formula for the molecule shown below.
Identify the hybridization of each carbon atom.
Identify the most polar bond in the molecule and show the direction of its polarity.
C9H8O
6a. (15 points) From the acid/base pairs shown below, write a complete balanced reaction and indicate whether the preferred direction of the equilibrium is to the right or left. Refer to the table of pKa values on the last page.
acid base
6b. (10 points) Use the table of pKa values (last page) to estimate the pKa values of the two functional groups found in alanine (shown below). Draw a structure that illustrates the state of ionization expected for alanine in water at pH 7.
COOH group about pKa = 5
NH2 group about pKa = 25
(or NH3+ group about pKa = 10)
at pH 7, the NH2 group will be protonated
and the COOH group will be deprotonated
7. (20 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Indicate stereochemistry if it is specific. Also indicate the general reaction type: substitution, elimination, addition, oxidation, reduction, or other.
Reaction Type
a) 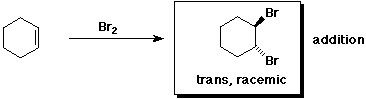
b) 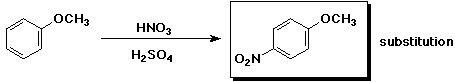
c) 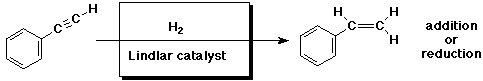
d) 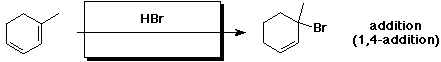
e) 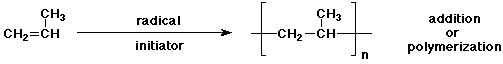
8. (20 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the final major product. Indicate stereochemistry if it is specific. Also identify the most likely mechanism for the reaction.
Product / / Mechanism
a) 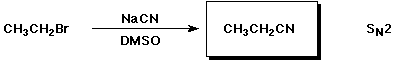
b) 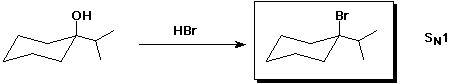
c) 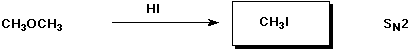
d) 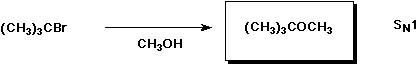
e) 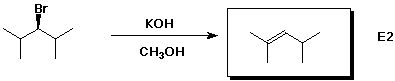
9. (15 points) The following sequence could be used to synthesize a specific deuterium-labeled benzoic acid. Complete all the missing parts of the reaction sequence.

10. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the chlorination of toluene using FeCl3 as catalyst. Just show the pathway to the formation of p-chlorotoluene. Show all steps and write all resonance forms for any intermediates involved.
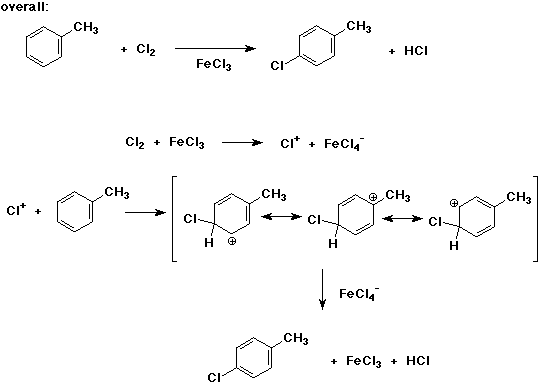
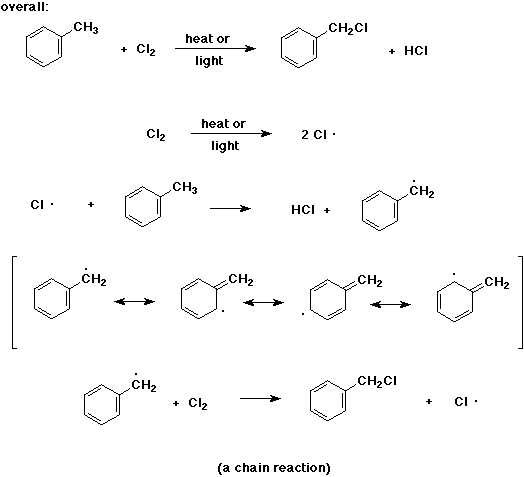
11. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the free radical chlorination of toluene using heat or light as catalyst. Just show the pathway to the formation of benzyl chloride. Show all steps and write all resonance forms for any intermediates involved.
Potentially useful information:
pKa values
HCl / / -7
CH3OH2+ / / -2
H3O+ / / -1.7
HF / / 3
CH3COOH / / 5
NH4+ / / 10
phenol / / 10
CH3OH / / 15.5
H2O / / 15.7
(CH3)3COH / / 18
NH3 / / 25