![]()
![]()
Carroll, pp 386 - 393: # 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8G, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16G, 17G, 18G, 20
( G means a graph will be necessary to illustrate the full details of the problem)
1. Indicate the compounds you would prepare and the experiments you would run in order to determine the primary kinetic isotope effect for the bromination of acetone.
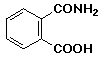
2. Hydrolysis of phthalamic acid, shown below, which is specifically C-13 labeled at the amide carbonyl carbon, gives phthalic acid with label equally incorporated into both carboxyl groups. Explain with a mechanism. Indicate an important control experiment that should be performed with phthalic acid.
3. If the nitration of toluene is carried out with nitric acid in nitromethane solvent, the rate of the reaction is exactly the same as the nitration of benzene under the same conditions. Nevertheless, if an equimolar mixture of benzene and toluene undergoes nitration in nitromethane solvent, nitrotoluene is formed much more rapidly than nitrobenzene. Explain the apparent paradox here, using a mechanism, a kinetic rate law, and a potential energy diagram.