Chem 336 - Spring 1999 - Organic Chemistry III
Portland State University - Dr. Carl C. Wamser
Exam 3
1. (25 points) Write complete structures for the following, including clear indications of the appropriate stereochemistry for the naturally-occurring compounds:
a) leucylproline at pH 7
b) the ethyl ester of arginine at pH 7
c) GTP at pH 10
d) deoxycytidine-3'-monophosphate
e) D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
2a. (5 points) In the fermentation of glucose to ethanol and CO2, which carbons become the CO2 ? (Identify them by numbers from the original glucose.)
2b. (5 points) If the following nucleic acid were treated with an excess of the reagents necessary for the excision of any pyrimidine bases, what fragments would remain?
5'-GGTAAGCATAG-3'
3. (10 points) Identify the unknown polypeptide based on the following information:
* complete hydrolysis gives equimolar amounts of Ala, Cys, His, Lys, Tyr, and Val
* the N-terminus is identified as His
* chymotrypsin hydrolysis gives two tripeptides, A and B
* A contains Ala, His, and Tyr
* trypsin hydrolysis gives a pentapeptide plus Cys
4. (10 points) Write the keto and the enol forms of guanine, and indicate the protonated form that could serve as an intermediate between them.
5. (15 points) Illustrate the steps in a synthesis of the dipeptide TrpPhe, assuming that the pure amino acids are available, along with BOC as a protecting agent and DCC as a coupling agent.
6. (15 points) In the process of photosynthesis, the uptake of CO2 occurs in the step shown below. Follow the carbons through these two steps by numbering them - use the standard numbering for the ketopentose and call CO2 carbon 6.
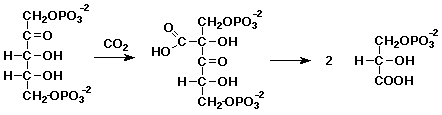
Is either reaction an oxidation or reduction?
Indicate what would be needed to balance each reaction.
7. (10 points) Show how NAD+ can be used to oxidize an alcohol, using electron-pushing arrows to represent the movements of electron pairs.
8. (5 points) Pick any molecule you'd like and explain how its chemical structure (write it out) makes it particularly well-suited for its biological function.