Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring Term |
Exam 3 |
![]()
Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring Term |
Exam 3 |
![]()
1. (25 points) Write complete structures for each of the following, including stereochemistry:
a) BOC-Phe-Pro at pH 7
b) 5'-ATP
c) the C-1 monoglyceride of 9,12-octadecadienoic acid, with (R) stereochemistry
d) a C-G base pair - just show the bases with the specific H-bonding
e) a cyclic dipeptide (Ala)2
2. (15 points) Arrange the lists below in order, indicating MOST and LEAST under the compounds with the highest and lowest values of the property indicated.
a) number of stereocenters
![]()
b) number of carbon atoms
![]()
c) pI values
![]()
d) water solubility
![]()
e) amount of positive charge at pH 7
![]()
3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by writing the structure of the expected product, including stereochemistry.
a) ![]()
b) 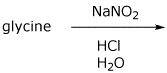
c) 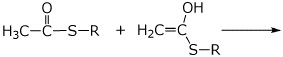
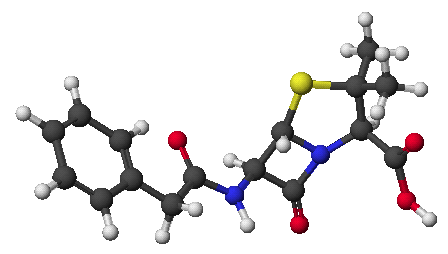
d) 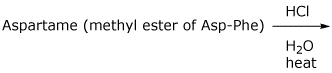
e) 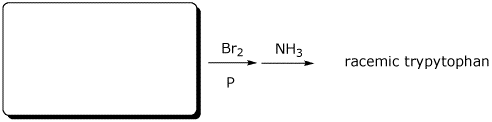
4. (15 points) Geranyl diphosphate is the precursor to several monoterpenes, including limonene and the pinene isomers, shown below. Write mechanisms to show how the three products are formed. Track the carbons using the numbering scheme shown.
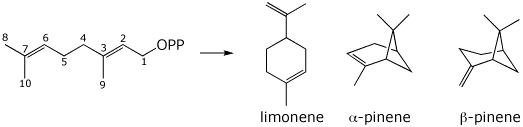
5. (18 points) Identify the unknown heptapeptide based on the information below.
Complete hydrolysis gives only six different amino acids: Arg, Asp, Cys, Lys, Ser, Tyr
Edman's reagent releases Cys followed by Asp
Carboxypeptidase releases Cys
Trypsin cleavage releases two tripeptides and Cys
Chymotrypsin cleavage releases a pentapeptide and a dipeptide, Arg Cys
Using only the side chains of the amino acids above, illustrate each of the following interactions. Write out the complete side chains and their interaction.
a) covalent bonding
b) Coulombic attraction
c) Coulombic repulsion
d) hydrogen-bonding (using uncharged side chains)
6. (12 points) NADH is a dinucleotide commonly used as a reducing agent, for example, in the general reaction shown below.
Using the structures below, show how a ketone would be reduced by NADH. Show all electron-pushing arrows and indicate where an acid catalyst would be effectively used.
Conversely, NAD+ is a common oxidizing agent.
Show the reverse reaction, oxidation of a secondary alcohol to a ketone, using similar structures and all electron-pushing arrows.
Would an acid catalyst be effective here? Show how an effective catalyst would be used.