Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring 2009 |
Exam 3 Answer Key |
![]()
Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring 2009 |
Exam 3 Answer Key |
![]()
1. (25 points) Write accurate structures for the following, including clear stereochemistry:
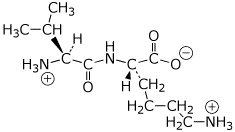
a) valyllysine (at pH 7)
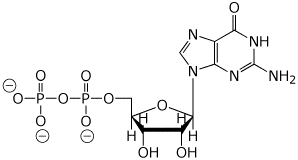
b) guanosine 5’-diphosphate (at pH 10)
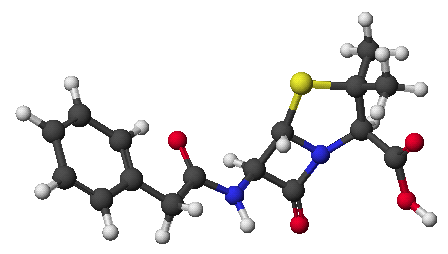
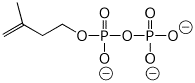
c) isopentenyl pyrophosphate (at pH 10)
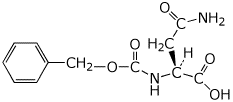
d) CBZ-protected asparagine (at pH 7)
e) C-1 monoglyceride of octadecanoic acid with R stereochemistry at C-2
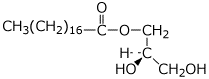
2. (16 points) Complete the following reactions by writing the missing structures, complete with accurate stereochemistry.
a) 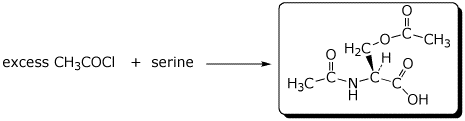
b) 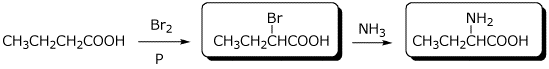
c) 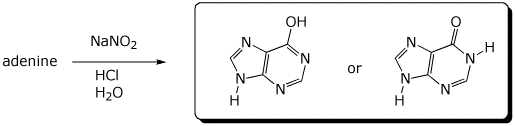
d) 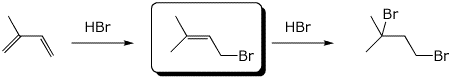
3. (15 points) The pKa values for arginine are 2.17, 9.04, and 12.48 .
Write a pH scale divided into four regions and identify the major structure of arginine expected in each region.
You may ignore stereochemistry.
pH < 2.17
2.17 < pH < 9.04
9.04 < pH < 12.48
12.48 < pH
Predict an approximate value for the pI of arginine.

4. (15 points) Write the structures of the components that would be expected upon complete hydrolysis in acid. Include stereochemistry and the correct charges for pH ~1. Show sugars in open-chain form.
a) 2'-deoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate
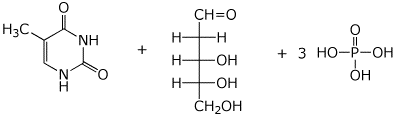
b) Gln-Gly-Trp
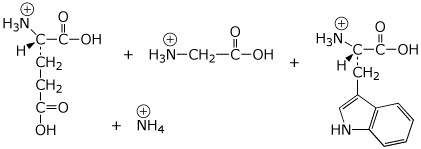
c) 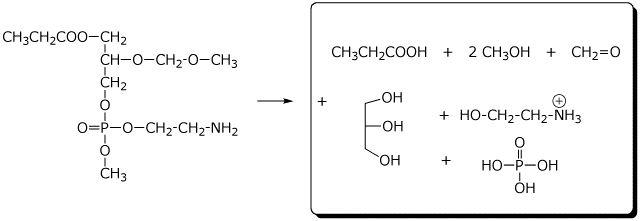
5. (18 points) Identify the unknown hexapeptide based on the following data.
Complete hydrolysis gives one equivalent each of Arg, Asp, Phe, Trp and 2 Cys
Edman degradation releases Cys
Carboxypeptidase releases Trp
Chymotrypsin cleavage gives a tetrapeptide and the dipeptide Cys-Trp
Trypsin cleavage gives a tetrapeptide and a dipeptide
Cys-Arg-Asp-Phe-Cys-Trp
Using only the amino acids found in the hexapeptide above, give examples of side chain interactions that illustrate the following.
Write the complete side chains and show the specific interaction.
a) covalent bonding
![]()
b) H-bonding attractions
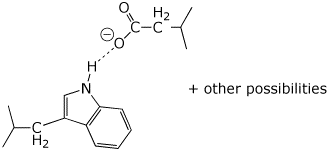
c) Coulombic (charge) attractions
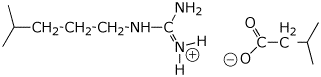
d) hydrophobic interactions
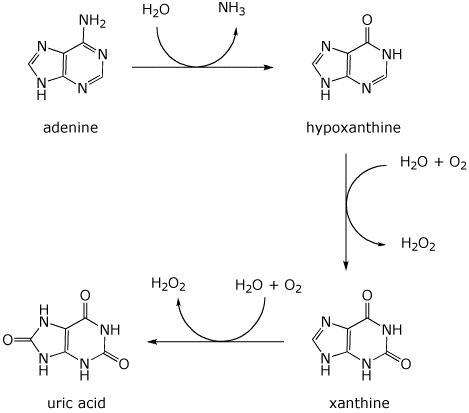
6. (11 points) Adenine is excreted by oxidation to uric acid, following the pathway below.
Balance each of the three steps by adding the appropriate compounds at the three curved arrows.
The new oxygen atoms come solely from H2O or O2.
When O2 is used as an oxidant in aqueous solution, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is the byproduct.