Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring 2007 |
Exam 1 |
![]()
Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring 2007 |
Exam 1 |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write accurate names for the following:
a) 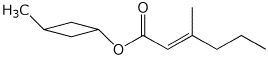
b) 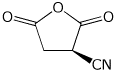
c) 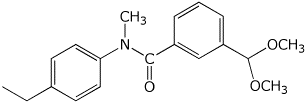
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) potassium p-cyanophenylacetate
b) the best resonance form of the enolate anion from 1,3-cyclohexanedione
c) the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky product from 2-methylpentanoic acid
d) the anionic tetrahedral intermediate in the hydrolysis of benzamide
e) the transition state for decarboxylation of malonic acid
3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by writing the structure of the expected major product:
a) 
b) 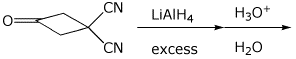
c) 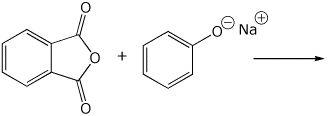
d) 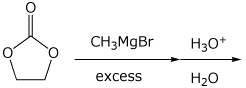
e) 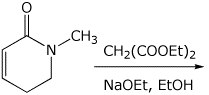
4. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed reaction shown below. Show all steps and all resonance forms for any intermediates involved.
5. (10 points) Show how to prepare the compound below using a malonic ester synthesis.
6. (15 points) The sequence of reactions shown below result in the formation of a lactone. Write a reasonable mechanism.
7. (15 points) A typical biological reaction using a thioester is illustrated in simple form below.
Without any catalyst, direct addition would lead to a zwitterionic tetrahedral intermediate. Write its structure.
With enzymatic catalysis, the two reactants are not only placed in proper orientation (as shown below), but BOTH acid and base catalysis are provided to avoid the formation of a high-energy zwitterion. Show where an acid and a base catalyst would be effectively located in order to go directly to a neutral tetrahedral intermediate.
From the neutral tetrahedral intermediate, show where acid and base catalysis would be used to go directly to the two neutral products.