Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring 2006 |
Exam 1 |
![]()
Organic Chemistry III |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 336 - Spring 2006 |
Exam 1 |
![]()
1. (15 points) Give complete names for each of the following:
a) 
b) 
c) ![]()
2. (15 points) Give complete structures for each of the following:
a) p-cyanobenzoyl chloride
b) isobutyl cyclopentanecarboxylate
c) hexanedioic anhydride
d) the best resonance form for the enolate of malonic ester
e) N-cyclobutyl-N-methylformamide
3. (15 points) Indicate the relative order of the following series of compounds with respect to the property listed. Write “MOST” and “LEAST” under the compounds with the highest and lowest values, respectively.
a) acidity
b) acidity
c) basicity
d) ease of hydrolysis
e) ease of decarboxylation
4. (15 points) Complete the following table for the reactions indicated.
a) ester hydrolysis ( RCOOR’ + H2O )
neutral tetrahedral intermediate
conjugate base of tetrahedral intermediate
conjugate acid of tetrahedral
intermediate
(two different forms)
final products
b) amide hydrolysis ( RCONHR’ + H2O )
neutral tetrahedral intermediate
conjugate base of tetrahedral intermediate
conjugate acid of tetrahedral
intermediate
(two different forms)
final products
c) amide formation from an acid chloride ( RCOCl + NH3 )
neutral tetrahedral intermediate
conjugate base of tetrahedral intermediate
conjugate acid of tetrahedral
intermediate
(two different forms)
final products
5. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the major product.
a) 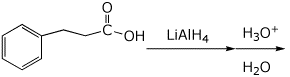
b) 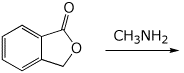
c) 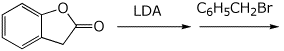
d) 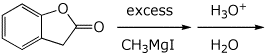
e) 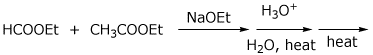
6. (15 points) The following retrosynthetic analysis was developed for the preparation of valine, an amino acid. Show all the steps that would be needed in the synthesis, starting from acetone and ethyl acetate.

7. (10 points) The malonic ester synthesis can be modified by using
an epoxide instead of an alkyl halide, in which case a lactone is formed.
Show a complete mechanism for just the first stage of the synthesis (up
to the enolate anion shown in brackets below). Show all steps and show
all resonance forms for any intermediates involved.
