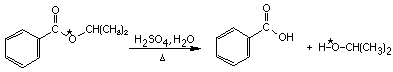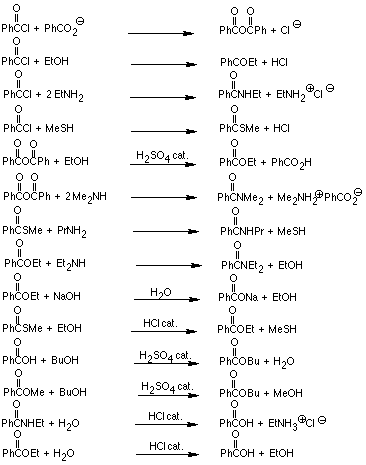Carboxylic Acids

1. Specify the member of each of the following pairs that is more acidic.
Explain your choice in words and with the help of
structures.
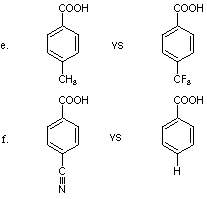
a. CH3COOH vs FCH2COOH
b. CF3COOH vs CCl3COOH
c. CH2=CHCH2COOH vs HC=CCH2COOH
d. NCCH2COOH vs HC=CCH2COOH
2. The ester shown is labeled with oxygen-18 as indicated (*O=18O). Give a mechanism consistent with the labeling results
shown when the ester is hydrolyzed in unlabeled water at pH = 2.
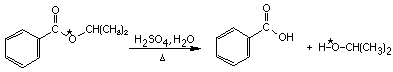
3. Each of the following reactions involve nucleophilic substitution at
an acyl carbon (carbonyl of a carboxylic acid or derivative) by way of
a tetrahedral addition intermediate. Write a general mechanistic scheme
(use curved arrows to show movement of electron pairs) for these reactions,
keeping in mind that acid and base catalyzed processes will differ in timing
of proton transfers. Construct a table showing the electrophile and the
nucleophile in the key bond-forming step and the corresponding tetrahedral
addition intermediate for each reaction.
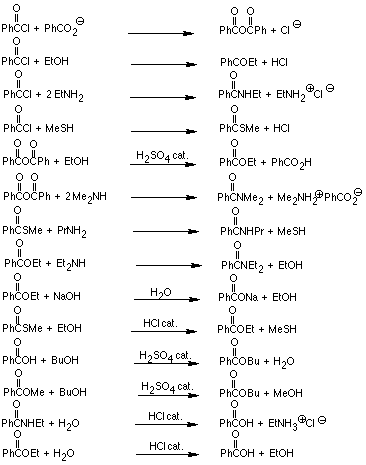
Materials adapted from:
Peer-Led Team Learning: Organic Chemistry, 1/e
Jack A. Kampmeier, University of Rochester
Pratibha Varma-Nelson, St. Xavier University
Donald Wedegaertner, University of the Pacific
Prentice-Hall, 2001, ISBN 0-13-028413-0
http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~chemwksp/OrganicChem.html


![]()