
Lipids

Lipids
- general term for biomolecules that are water-insoluble but soluble
in organic media
(in biological systems this usually means membrane-bound)
- categories of lipids:
- fatty acids - long chain carboxylic acids (C12 -
C20)
- fats and oils - triesters of fatty acids and glycerol (triglycerides)
(monoglycerides are monoesters, diglyecrides are diesters)
(function as energy storage materials)
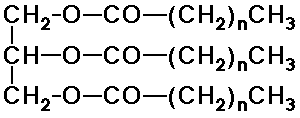
- phosphatides - phosphate esters of glycerol (+ fatty acids)
(membrane constituents)
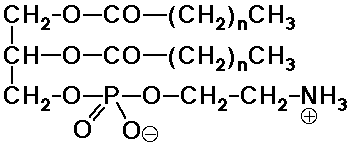
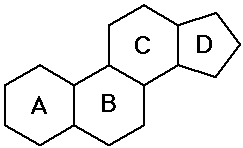
- steroids - polycyclic structure with specific substituents
(hormones, special functions)
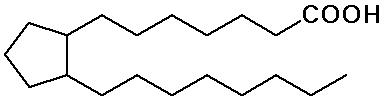
- prostaglandins - cyclic structure with long chains
(hormones, special functions)
Fats and Oils
- fats are solids, oils are liquids (same basic triglyceride structure)
- serve as insoluble deposits that can be retrieved for energy
Fatty Acids
- all natural fatty acids have an even number of carbon atoms, since
they are synthesized from acetate (C2) subunits
- natural unsaturated fatty acids have cis double bonds
cis-double bonds lead to a lower melting point
unsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are also more easily digestible
Soaps
- basic hydrolysis of fats (saponification) generates soaps
(the sodium salts of fatty acids)
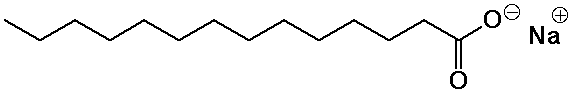
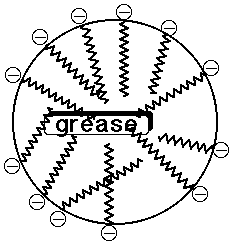
- the ionic head group is water-soluble, the nonpolar tail insoluble
- soaps tend to aggregate in micelles, where nonpolar dirt dissolves
Phospholipids
- the natural analog of the soap structure:
a polar phosphate head group
two nonpolar tails
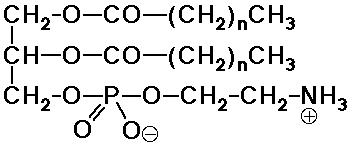
Bilayer Lipid Membranes
- phospholipids with two tails tend to make planar bilayer aggregates
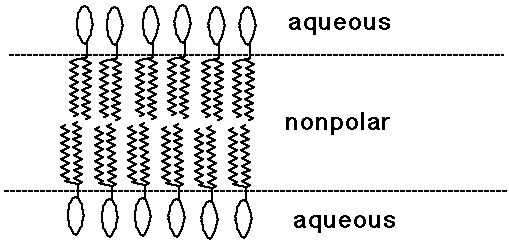
- other lipids are found in the nonpolar environment of membranes
- proteins often have a nonpolar and polar part, and are membrane-bound
Steroids
- cholesterol is the precursor to most other steroids: vitamin D,
bile salts, hormones
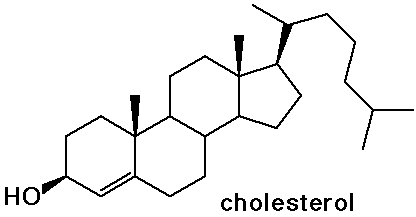
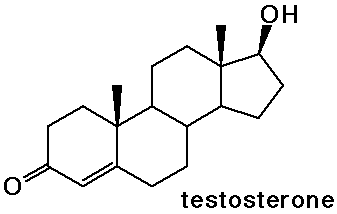
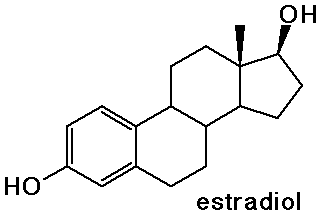
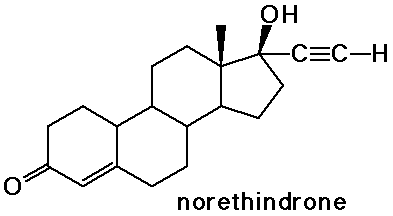
- the sex hormones and birth control pills are steroids
![]()

![]()
![]()