 |
Organic
Chemistry III
|
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chapter 21 Notes |
Chem 336 - Spring 2005 |
![]()
 |
Organic
Chemistry III
|
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chapter 21 Notes |
Chem 336 - Spring 2005 |
![]()
![]()
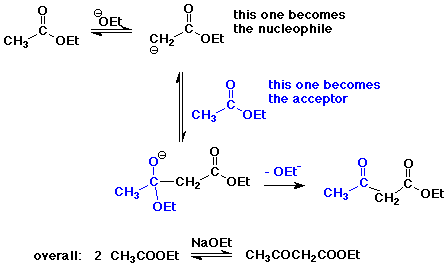
The Claisen Condensation
Decarboxylation of beta-ketoacids
Acetoacetic Ester and Malonic Ester Syntheses
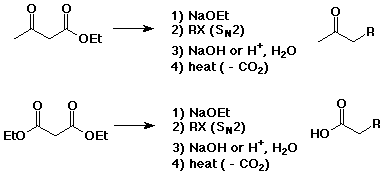
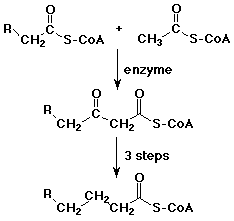
Biological Claisen Reactions