
Organic Chemistry III
Professor Carl C. Wamser

Chapter 25 Workshop Problems
Organic Chemistry III |
||
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry III |
||
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
![]()
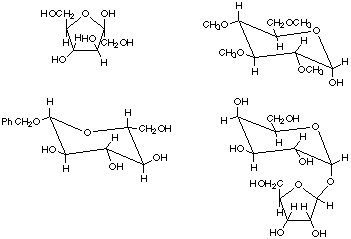
1. Show the cyclic structures indicated that are in equilibrium with the open chain sugars represented in the Fischer projections. Show six-membered rings in the chair conformations.

2. Sophorose is a disaccharide (found in some bean varieties) in which the C-4 OH of a D-glucopyranose unit forms a beta linkage to the anomeric carbon of a D-galactopyranose unit.
a. Provide a structure of sophorose in which the rings of the sugar are shown in the chair form. Indicate clearly whether substituents are axial or equatorial.
b. Is sophorose a reducing sugar or not? Why or why not?
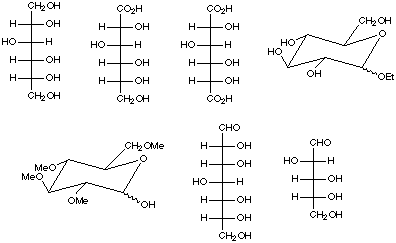
3. Identify the following as nonreducing or reducing sugars and clearly justify
your choices. Circle the functional group(s) responsible for these properties.
4. Show how to convert D-glucose into the following molecules using any necessary reagents. If more than one synthetic step is required, give the product for each step. Clearly specify all reagents and conditions.
Peer-Led Team Learning: Organic Chemistry, 1/e
Jack A. Kampmeier, University of Rochester
Pratibha Varma-Nelson, St. Xavier University
Donald Wedegaertner, University of the Pacific
Prentice-Hall, 2001, ISBN 0-13-028413-0
http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~chemwksp/OrganicChem.html