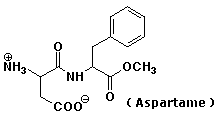
Organic Chemistry III
Professor Carl C. Wamser

Exam 3
Organic Chemistry III |
||
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry III |
||
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
![]()
1. (20 points) Write complete structures for each of the following, including stereochemistry.
a) sucrose
b) b-L-glucose (in a Haworth projection)
c) N,N-dimethyl-b-N-glycoside of D-2-deoxyribose
d) a C-1 monoglyceride of palmitoleic acid (C16, monounsaturated)
e) seryltyrosine (at pH 7)
2. (20 points) Write complete structures for each of the following, including stereochemistry.
a) BOC-N-protected cysteine (at pH 7)
b) the C-2 epimer of D-glucose in a b-pyranose chair form
c) isopentenyl pyrophosphate (at pH 7)
d) the polycyclic ring structure of a steroid (just the rings)
e) the fundamental structural features of a prostaglandin
3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the expected final major product, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the original starting material. Show the complete structure with stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 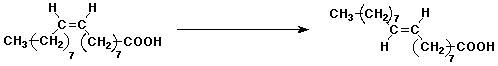
b) ![]()
c) 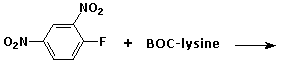
d) ![]()
e) ![]()
4. (12 points) For the pentapeptide Ala-Arg-Cys-Pro-Trp indicate the peptides and/or amino acids that would be formed and/or affected upon treatment with each of the following reagents:
a) Edman’s reagent
b) carboxypeptidase
c) trypsin
d) chymotrypsin
e) partial hydrolysis to give dipeptides (list all four possibilities)
5. (8 points) The synthetic sequence below is used to prepare an amino acid.
Which amino acid would be formed?
Is it possible to use this sequence of reactions to prepare the enantiomerically pure L-amino acid?
If so, explain
what stereochemistry of the reactants would be required.
If not, explain
why not.
6. (10 points) Show all the steps in the mechanism
of the reaction shown below. Use electron-pushing arrows.
Show where an enzyme might use base catalysis and/or acid catalysis
to facilitate this reaction.
7. (15 points) Write the structures of all the products that would be formed upon complete hydrolysis of each of the following. Write sugars in their open-chain form.
a) 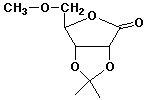
b) 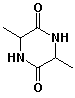
c) 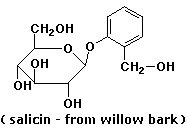
d) 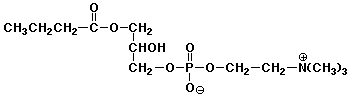
e)