Organic Chemistry III
Dr. Carl C. Wamser
1. (20 points) Write complete structures for the following, including clear indications of the appropriate stereochemistry:
a) asparagine at pH 7
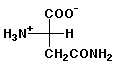
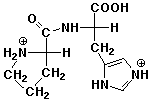
b) Pro-His at pH 1
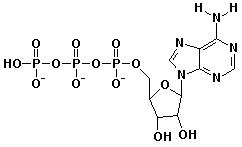
c) ATP at pH 5
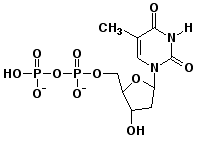
d) deoxythymidine-5'-diphosphate
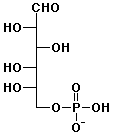
e) L-glucose-6-phosphate
2. (12 points) Follow the base-pairing in the strands of the different nucleic acids as indicated. Clearly indicate the directionality of the polymer chains.
DNA strand 1: 5' - A G T G C A A T C G A T - 3'
DNA strand 2: 3' - T C A C G T T A G C T A - 5'
mRNA:
(complementary to 5' - A G U G C A A U C G A U
- 3'
DNA strand 2)
tRNAs:
(4 of them) U C A , C G U , U A G , C U A ( all
from 3' to 5' )
tetrapeptide
synthesized: N - Ser - Ala - Ile - Asp - C
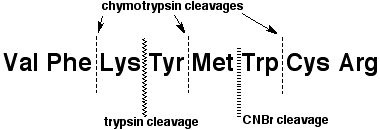
3. (16 points) Identify the unknown octapeptide based on the following information:
* complete hydrolysis gives equimolar amounts of
Arg, Cys, Lys, Met, Phe, Trp, Tyr, and Val
* Edman degradation releases Val
* chymotrypsin hydrolysis gives four dipeptides - A, B, C, and D
* A contains Arg and Cys, B contains Lys and Tyr
C contains Met and Trp, and D contains Phe and Val
* trypsin hydrolysis gives a pentapeptide E and a tripeptide F
* F contains Phe, Lys and Val
* CNBr cleavage gives a pentapeptide G and a tripeptide H
* H contains Arg, Cys and Trp
Identify each of the lettered peptides as well as the complete octapeptide.
Val Phe Lys Tyr Met Trp Cys Arg
A = Cys Arg, B = Lys Tyr, C = Met Trp, D = Val Phe
E = Tyr Met Trp Cys Arg, F = Val Phe Lys
G = Val Phe Lys Tyr Met, H = Trp Cys Arg
4. (12 points) The pKa values for aspartic acid are 2.10, 3.86, and 9.82 , and the isoelectric point is 2.98. Illustrate the major structures expected at each of the following pH values, and indicate whether the amino acid would be expected to migrate towards the cathode (-) or the anode (+) in an electrophoresis experiment at that pH.
a) pH 1.5
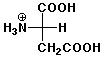
overall + charge, moves towards cathode
b) pH 4.5
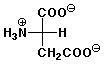
overall - charge, moves towards anode
c) pH 10.5
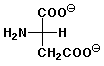
overall - charge, moves towards anode
5. (15 points) Some of the mRNA codons were determined by using synthetic polynucleotides and observing the polypeptides that were synthesized. Indicate what amino acids would be expected in the polypeptides synthesized based on the following polynucleotides (mRNAs). Assume the chains are long enough to have all possible combinations.
a) poly A (i.e., AAAAAAAAAAA )
AAA codes for Lys
b) poly G
GGG codes for Gly
c) poly C
CCC codes for Pro
d) poly U
UUU codes for Phe
e) a regularly alternating copolymer of A and C (i.e., ACACACACA.. )
ACA codes for Thr
CAC codes for His
f) a random copolymer of A and C
AAA codes for Lys
AAC codes for Asn
ACA codes for Thr
CAA codes for Gln
CCA codes for Pro
CAC codes for His
ACC codes for Thr
CCC codes for Pro
6. (15 points) The body stores energy in the form of fats by building up fatty acids from acetyl CoA, as shown in the steps below. For each one of the four steps,
a) write a balanced reaction, adding appropriate cofactors
as needed
b) describe the overall reaction
c) identify any stereochemistry
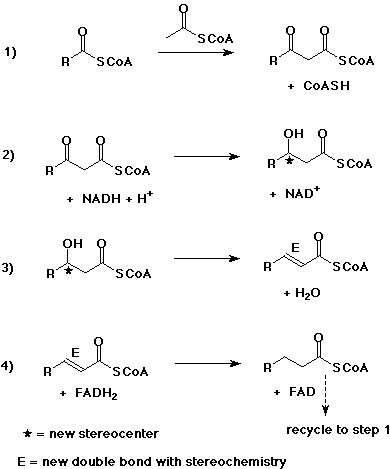
Step 1 is a Claisen condensation.
Step 2 is a reduction of a ketone to a secondary alcohol.
Step 3 is a dehydration.
Step 4 is a reduction of an alkene to a saturated chain.
7. (10 points) Show that fats contain more energy than carbohydrates by balancing the reactions shown below, where glucose (C6H12O6) represents a typical sugar and hexanoic acid represents a typical fatty acid with the same number of carbon atoms (C6H12O2). Calculate how many moles of NADH could be generated in each case (use NAD+ as the only oxidant rather than FAD).
Hint - first balance all the atoms except H
C6H12O6 ----> 6 CO2
C6H12O2 ----> 6 CO2
C6H12O6 + 6 H2O + 12 NAD+ --> 6 CO2 + 12 NADH + 12 H+
C6H12O2 + 10 H2O + 16 NAD+ --> 6 CO2 + 16 NADH + 16 H+
Fats are more highly reduced than sugars and need more oxidation to become CO2.