
Chapter 15 Homework Answers

Brown & Foote, pages 581 - 592 :
Problems 15.14 - 22, 24 - 27, 31 - 35, 41, 44 - 52, 57 - 65
1. Write complete names for each of the following:
a) 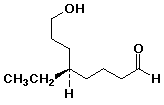
(R)-5-ethyl-8-hydroxyoctanal
b) 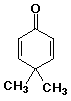
4,4-dimethyl-2,5-cyclohexadienone
2. Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation
of the cyclic acetal between acetone and cis-1,2-cyclopentanediol.
Explain why an acetal is not formed with the trans isomer.

It is sterically difficult for the trans-1,2-diol to get both
OH groups to connect to the same carbon of acetone.
3. Develop a synthetic sequence for 3-ethyl-3-hexanol that uses
as organic starting materials only alcohols having four carbons
or fewer.

4. Explain how acetone in the presence of radioactively-labelled
water (H2O-18) slowly becomes radioactive
itself.
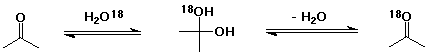
The hydration reaction (addition of water as a nucleophile) does
occur, although the equilibrium constant strongly favors acetone
rather than 2,2-propanediol. Reversal of the reaction could eliminate
either normal water or radioactive water.




