1. (15 points) Write a complete name for each of the following compounds, including designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 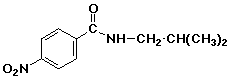
N-isobutyl-4-nitrobenzamide
b) 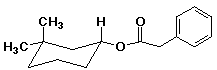
(R)-3,3-dimethylcyclohexyl phenylacetate (or phenylethanoate)
c) 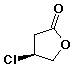
(S)-3-chloro-4-butanolactone
or
(S)-b-chloro-g-butyrolactone
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures that illustrate each of the following:
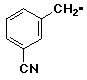
a) m-cyanobenzyl radical
b) the best resonance form for p-nitrophenolate anion

c) a beta-lactam

d) the anionic tetrahedral intermediate in the basic hydrolysis of formamide
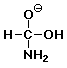
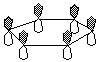
e) a picture of the lowest energy pi molecular orbital of benzene
3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Indicate stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 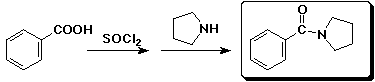
b) 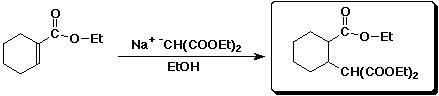
c) 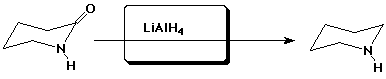
d) 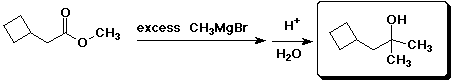
e) 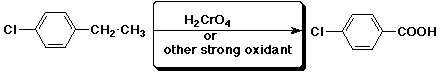
4. (15 points) Write the sequence of reaction steps that would be used in the conversion of cyclopentyl methyl ketone into its thermodynamically favored enolate anion, followed by its use in a directed aldol reaction with acetaldehyde to give the final product below.
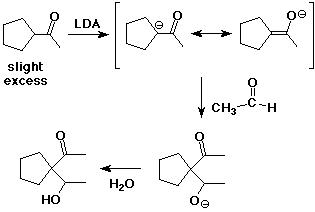
5. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed conversion of phenyl acetate into methyl acetate (a transesterification). Show all steps and all resonance forms for any intermediates involved.

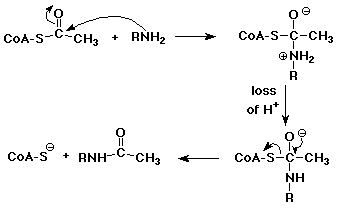
6. (15 points) Acetyl-CoA, abbreviated below, is often used in biological systems to transfer an acetyl group to O or N. Write a complete mechanism for the reaction that would be expected below; it occurs in aqueous solution at about neutral pH, so no acid or base catalysis is needed. Show all steps.
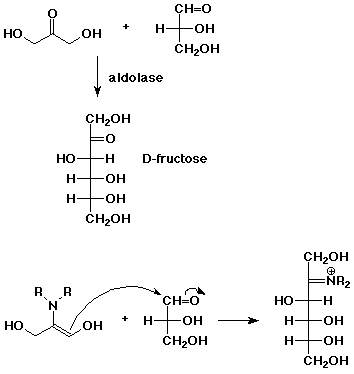
7. (10 points) Aldolase is an enzyme that catalyzes an aldol reaction, such as the one shown below. In fact, one carbonyl compound is first converted to an enamine before the reaction takes place. Show an enamine of the appropriate compound and show the reaction that forms the new bond.