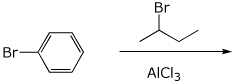Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter Term |
Final Exam Answer Key |
![]()
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter Term |
Final Exam Answer Key |
![]()
1. (25 points) Write complete names for the following compounds, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown.
a) 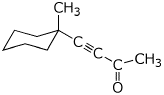
b) 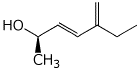
c) 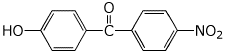
d) 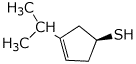
e) 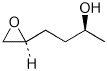
2. (15 points) Write complete structures for the following.
a) p-methoxybenzyl alcohol
![]()
b) the dimethyl enamine of cyclopentanecarbaldehyde
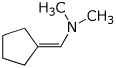
c) ethyl methyl sulfoxide with (R) stereochemistry
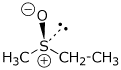
d) the HOMO of all-trans-2,4,6-octatriene
![]()
e) lithium diisobutylcuprate
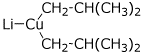
3. (15 pts) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write MOST and LEAST under the compounds with the highest and lowest values, respectively.
a) reactivity in a nitration reaction
![]()
b) acidity
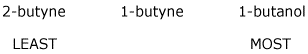
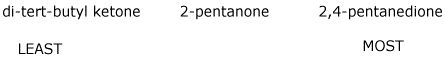
c) amount of enol at equilibrium
d) rate of hydrolysis in aqueous acid

e) number of different absorptions in the proton NMR spectrum
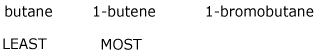
4. (15 pts) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting materials, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the expected major product.
a) 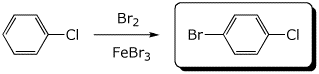
b) 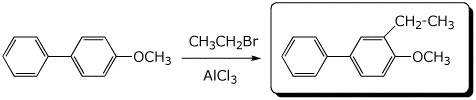
c) 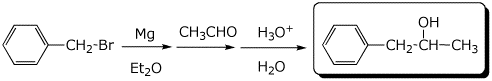
d) 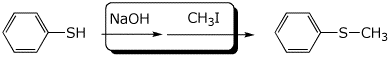
e) 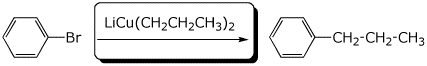
5. (15 pts) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting materials, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the expected major product.
a) 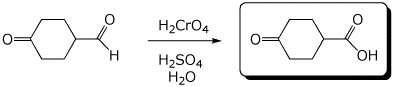
b) 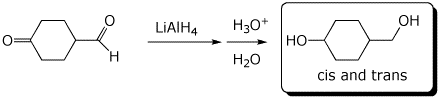
c) 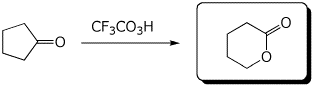
d) 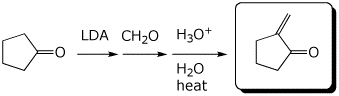
e) 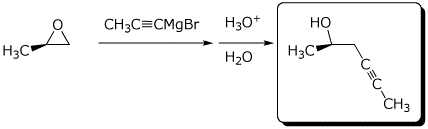
6. (20 points) Show how you would prepare each of the following target compounds, starting only from benzene and any alcohol with three or fewer carbons.
![]()
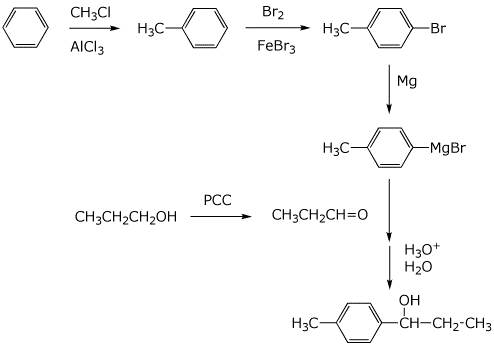
![]()
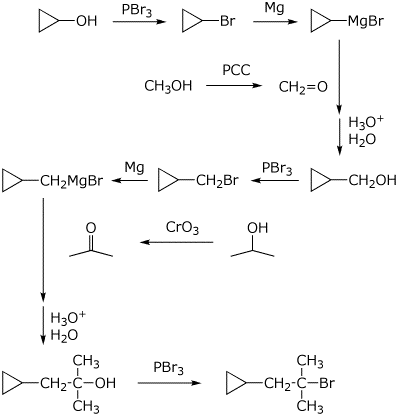
7. (15 points) Identify the unknown compound based on the information provided. For each piece of data, indicate what conclusions you can draw.
Molecular formula: C11 H15 Cl O
IHD = 4
Mass spectrum:
M+ at 198, M+2 peak at 200, with intensity about 1/3 that of M+
M= is for Cl-35 and M+2 is for Cl-37, isotopes that occur in 3:1 natural abundance
Infrared spectrum:
no significant peaks higher than 3100 cm-1
( no O-H groups )
no significant peaks in the 1700 - 1800 cm-1 range
( no C=O groups )
H-1 NMR spectrum:
7.0 ppm, 5H, multiplet - phenyl group with 5 H and one substituent
3.7 ppm, 2H, singlet - isolated -CH2- adjacent to O or Cl
1.9 ppm, 2H, quartet - -CH2- next to -CH3 , not adjacent to O or Cl
1.7 ppm, 3H, singlet - isolated -CH3 , not adjacent to O or Cl
1.1 ppm, 3H, triplet - CH3 next to -CH2-
( some other structures are also consistent )
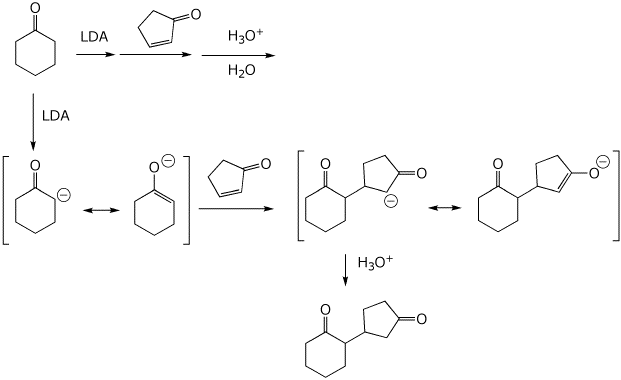
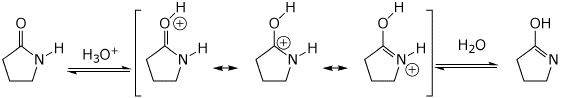
8. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the reaction shown below. Show all steps in the mechanism and all resonance forms for any intermediates. Use the correct forms for the predominant acid and base in the system at the appropriate time, i.e., do not use H+ and - H+. Electron-pushing arrows are optional.
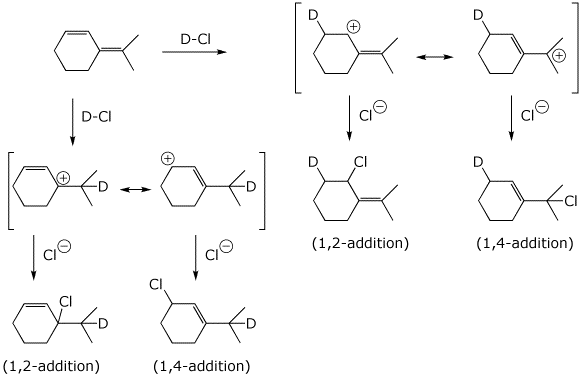
9. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the reaction shown below. Show all steps in the mechanism and all resonance forms for any intermediates. Electron-pushing arrows are optional. This mechanism should show two different allylic cations, each with two resonance forms, and four distinct products, consisting of 1,2- and 1,4- additions to each cation. Indicate the 1,2 and 1,4 products.
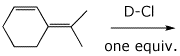
10. (20 points) The equilibrium shown below is similar to a keto-enol tautomerism, and can be catalyzed by either acid or base. Write two complete mechanisms for the reaction - in acid and in base. Show all steps in the mechanism and all resonance forms for any intermediates. Use the correct forms for the predominant acid and base in the system at the appropriate time, i.e., do not use H+ and - H+. Electron-pushing arrows are optional.
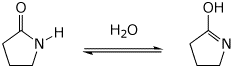
Acid-catalyzed:
Base-catalyzed:
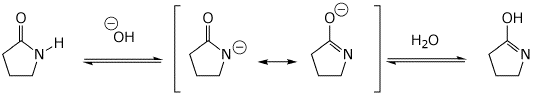
11. (10 points) Write a complete mechanism showing how the transformation below takes place. Show all steps and all resonance forms for any intermediates. Use electron-pushing arrows for each step.
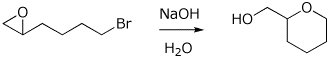
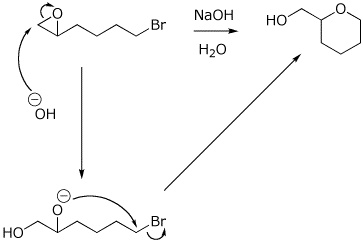
12. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the reaction shown below. Show all steps in the mechanism and all resonance forms for any intermediates. Show the pathway to the expected major product. Electron-pushing arrows are optional.