Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2008 |
Exam 2 |
![]()
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2008 |
Exam 2 |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write clear structures for each of the following:
a) (Z),(R)-4-hexen-2-ol
b) a chromate ester
c) an isobutyl Gilman reagent
d) the periodic acid cleavage products from 1,2-propanediol
e) sodium 4-nitrobenzenethiolate
2a. (5 points) Draw a typical quartet from a proton NMR spectrum and show where the chemical shift (d) and the coupling constant (J) would be measured.
2b. (5 points) Give a specific example of the 18-electron rule, explaining how your example fits the rule.
2c. (5 points) The formation of a vicinal diol
using tBuOOH and OsO4 is a syn addition.
Illustrate what this means in terms of the stereochemistry of the product
expected from cyclopentene. Draw the product(s) expected and designate
stereochemistry with R and S.
2d. (5 points) The formation of a vicinal
diol using tBuOOH and OsO4 is a syn addition.
Illustrate what this means in terms of the stereochemistry of the product
expected from
cis-2-butene. Draw the product(s) expected and designate stereochemistry
with R and S.
3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by writing the structure of the expected product:
a) ![]()
b) 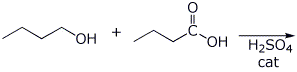
c) 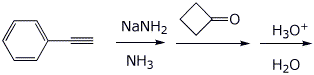
d) ![]()
e) ![]()
4. (20 points) Show how to prepare each of the compounds below using Grignard coupling reactions for the C-C bond-forming steps. All the carbons in the products must originate from alcohols having four or fewer carbon atoms. You may use any needed reagents or solvents.
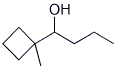
![]()
5. (15 points) Identify the unknown compound based on the data below.
molecular formula C9 H10 O2
What is the calculated IHD?
1H NMR :
a 9.9
ppm , 1 H , singlet
b 7.8
ppm , 2 H , doublet
c 6.9
ppm , 2 H , doublet
d 4.1
ppm , 2 H , quartet
e 1.4
ppm , 3 H , triplet
Identify by letter on your final structure each of the H absorptions above.
How many different peaks would be expected for this compound in its 13C
NMR spectrum?
6. (15 points) Identify the unknown compound based on the data below. It has IHD = 0.
Mass spectrum: molecular ion at 152 & 154 (approximately
equal intensity peaks)
additional
peaks at 107 & 109 (equal intensity)
largest
peak at 59
13C NMR: peaks at 70, 66, 30, and 15 ppm
1H NMR :
a 3.7
ppm , 2 H , triplet
b 3.5
ppm , 2 H , quartet
c 3.4
ppm , 2 H , triplet
d 1.2
ppm , 3 H , triplet
Identify by letter on your final structure each of the H absorptions above.
Identify each of the 13C peaks by reference to your structure.
Identify each of the peaks in the mass spectrum.