Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2008 |
Exam 1 Answer Key |
![]()
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2008 |
Exam 1 Answer Key |
![]()
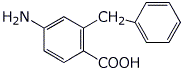
1a. (3 points) Write a clear structure for 4amino-2-benzylbenzoic acid
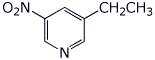
1b. (3 points) Write a clear structure for 3-ethyl-5-nitropyridine
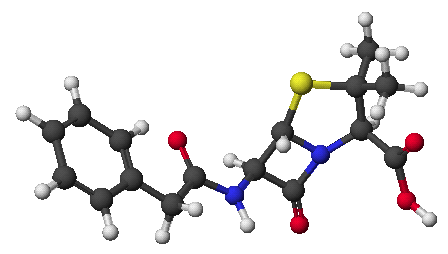
1c. (6 points) Write ALL the resonance forms (including Kekule forms) for
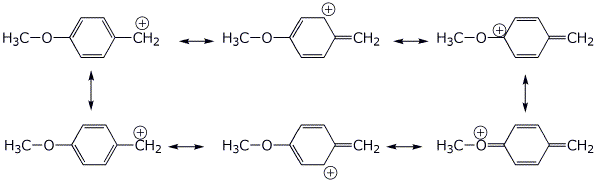
1d. (5 points) Write ALL the resonance forms (including Kekule forms) for
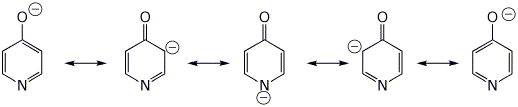
2. (15 points) Give brief definitions of the following terms and include a specific illustration.
a) s-cis vs s-trans (illustrate with 1,3-butadiene)

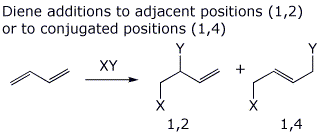
b) 1,2- vs 1,4-addition (illustrate with 1,3-butadiene)
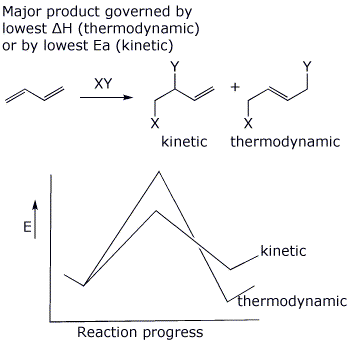
c) thermodynamic vs kinetic control (illustrate with 1,3-butadiene AND a potential energy diagram)
d) activator vs deactivator (illustrate with any appropriate pair of molecules)
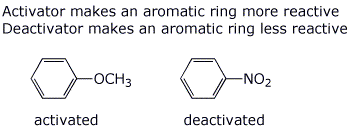
e) aromatic vs antiaromatic (illustrate with any appropriate pair of molecules)

3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by writing the structure of the expected product:
a) 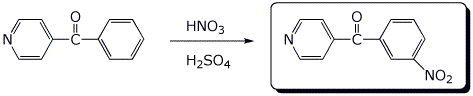
b) 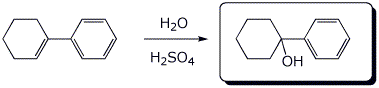
c) 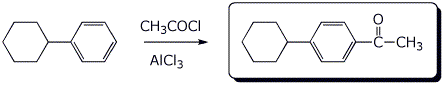
d) 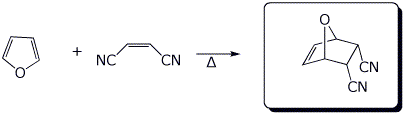
e) 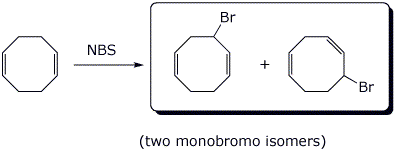
4a. (7 points) Write an energy level diagram, indicating the number of pi molecular orbitals expected, their relative energies, the number of electrons expected in each orbital, and identifying the HOMO and LUMO for the cation shown below.
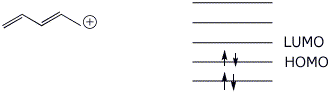
4b. (4 points) Draw approximate molecular orbital pictures of the HOMO and LUMO of the cation above, indicating orbital symmetries and the presence of any nodal planes.

5. (15 points) Isoprene, shown below, can react with one equivalent of HCl in a variety of ways.
a) Show the two possible 1,2-addition products that are constitutional isomers.
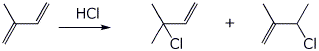
b) Show all the possible 1,4-addition products including E,Z stereoisomers.
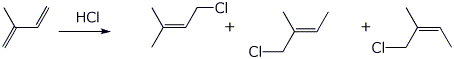
c) Show the 1,4-addition polymer that could be made from
isoprene in both its E and Z forms.
The Z form is natural rubber - indicate which one this is.
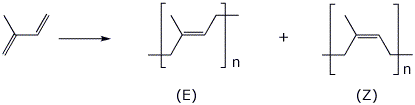
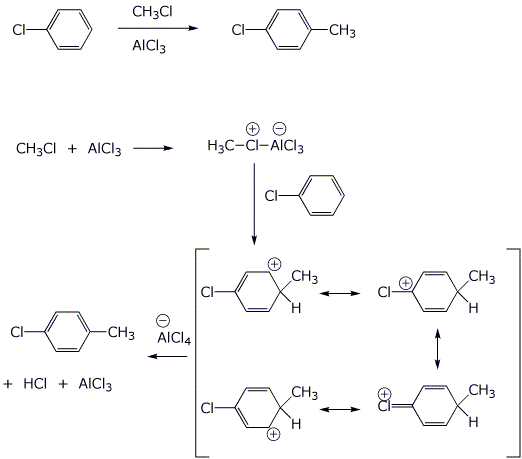
6. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the
Friedel-Crafts methylation of chlorobenzene.
Show all steps and all resonance forms for any intermediates involved.
Just show the pathway to the major product.
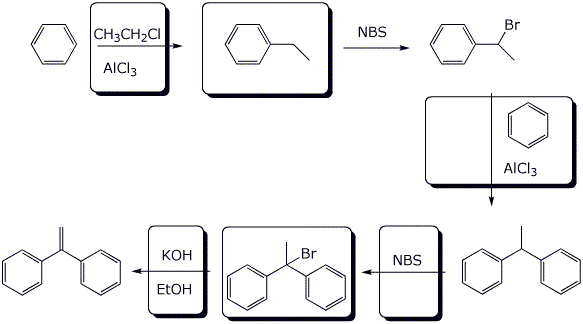
7. (12 points) Complete the following reaction sequence by filling in the boxes with the missing structures or reagents and conditions.