Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2007 |
Final Exam |
![]()
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2007 |
Final Exam |
![]()
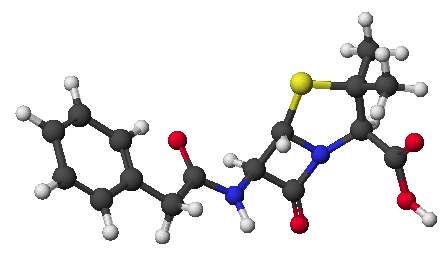
1. (25 points) Write complete names for the following:
a) 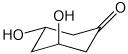
b) 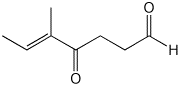
c) 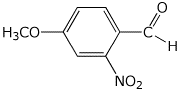
d) 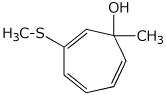
e) 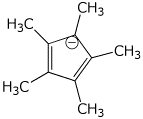
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) a chiral allene
b) 18-crown-6
c) the HOMO of 1,3,5-hexatriene
d) benzyl isobutyl disulfide
e) the hydrate of acetaldehyde
3. (15 points) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write MOST and LEAST under the compounds with the highest and lowest values, respectively.
a) reactivity towards electrophilic substitution
b) rate of HBr addition
c) polarity (amount of charge separation) of the bond
d) reactivity towards nucleophilic addition
e) rate of hydrolysis in aqueous acid
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by writing the missing part: either the necessary reagents and conditions or the structure of the expected major product:
a) 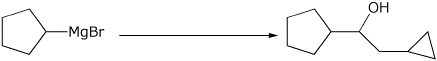
b) 
c) 
d) 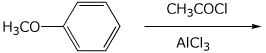
e) 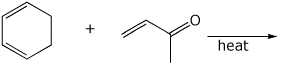
5. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by writing the missing part: either the necessary reagents and conditions or the structure of the expected major product:
a) 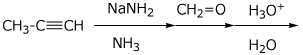
b) 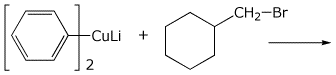
c) 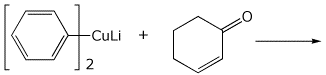
d) 
e) 
6. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the reaction shown below.
Show all steps, all resonance forms for intermediates, and all electron-pushing
arrows.
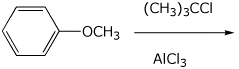
7. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the reactions shown below.
Show all steps and all resonance forms for intermediates.
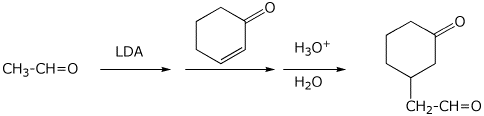
8. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis
shown below.
Show all steps, all resonance forms for intermediates, and all electron-pushing
arrows.
Do NOT use H+ or -H+ ; use the appropriate acid or base.
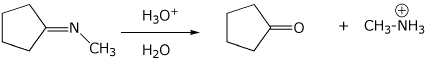
9. (15 points) Complete the following synthetic sequence by adding the reagents and conditions necessary at each step.
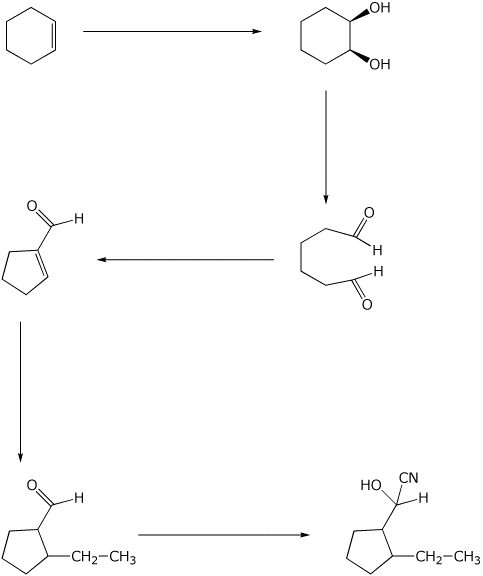
10. (20 points) Show how to synthesize the following compounds. As the source of the carbons in the final product, you may begin with any alcohol having four or fewer carbons and benzene.
a) 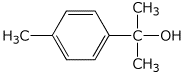
b) 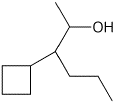
11. (20 points) The chiral epoxide below adds methanol to form two different regioisomers, depending on the conditions used.
The two regioisomers are 2-methoxy-1-phenylethanol (A) and 2-methoxy-2-phenylethanol (B).
In addition the products show different stereochemistry - either retained or inverted.
The two different conditions for the addition are either basic (NaOCH3 in CH3OH) or acidic (catalytic H2SO4 in CH3OH).
Write two different mechanisms (basic or acidic conditions) and clearly illustrate which case forms which regioisomer and whether the stereochemistry is retained or inverted.
Summarize in the table below.
Product (A or B) / / / Stereochemistry (retained or inverted)
Acidic conditions
Basic conditions
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Basic mechanism:
Acidic mechanism:
12. (15 points) Identify the unknown compound based on the data below and answer the questions about the data.
Molecular formula = C11 H14 O2
IHD = ____________
Infrared spectrum shows no absorptions in the range 3200-3600 cm-1 and a strong absorption at 1720 cm-1
Your conclusions based on the IR spectrum:
The 1H NMR spectrum shows five absorptions:
a 7.4 ppm , 5H , multiplet
b 3.6 ppm , 1H , quartet
c 3.3 ppm , 3H , singlet
d 2.5 ppm , 2H , singlet
e 1.9 ppm , 3H , doublet
Identify each of the absorptions with particular hydrogens in the compound.