Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2006 |
Exam 2 Answer Key |
![]()
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2006 |
Exam 2 Answer Key |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write accurate structures for each of the following.
a) isobutyl magnesium bromide
b) lithium dibenzylcuprate
c) any vicinal diol
d) diphenyl disulfide
e) trans-2-methylthiocyclopentanethiol
2. (15 points) Show clear electron-pushing arrows that illustrate how the following compounds are converted into the indicated products. WRITE ONLY ARROWS ON THIS PAGE.
a) 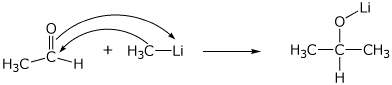
b) 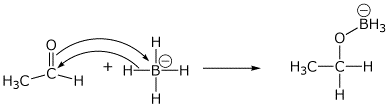
c) 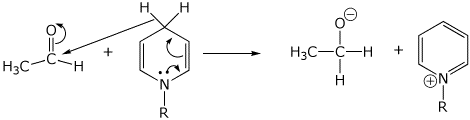
d) 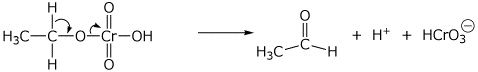
e) 
3. (15 points) Complete the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the final product or the necessary reagents and conditions.
a) 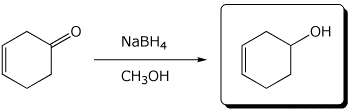
b) 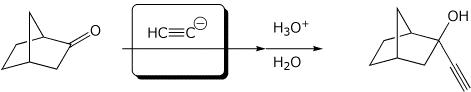
c) 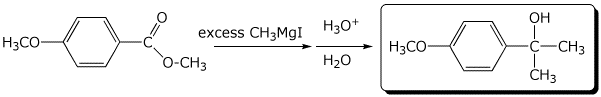
d) 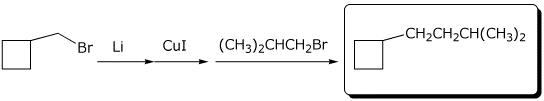
e) 
4. (20 points) Give clear explanations for the following:
a) (5 points) How can meta- and para-xylene (dimethylbenzene) be distinguished solely by C-13 NMR?
b) (5 points) What would be expected for the parent molecular ion peaks of CH2Br2 , assuming that the natural abundance of Br is equally Br-79 and Br-81? (Indicate expected m/z values with relative intensities.)
c) (10 points) How can each of the following isomers of C3H6O be distinguished solely by IR?
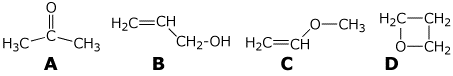
A will have a C=O stretch
B will have an O-H stretch ( and C=C )
C will have C=C and sp2 C-H stretches (but no O-H)
D will have none of the above absorptions
5. (20 points) Show reaction sequences that could be used to efficiently prepare the following two compounds. You must start with alcohols having four carbons or fewer.

The two reactants above could be reversed, i.e., n-butylcuprate + cyclopropylmethyl bromide.
There are also numerous possibilities using Grignard reactions, followed by removal of the resultant alcohol, e.g.,
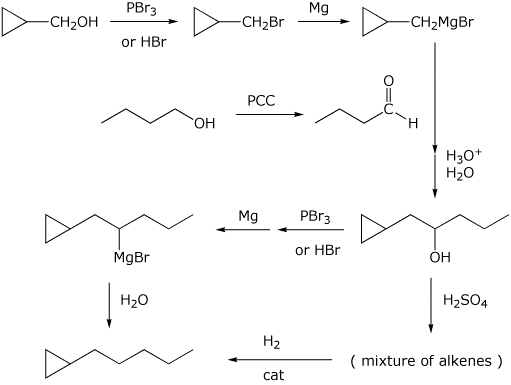

6. (15 points) Identify the unknown compound that is formed by reaction of phenyllithium with ethylene oxide and gives the spectral data below. Indicate what can be concluded from each piece of data, and assign the C-13 and H-1 NMR absorptions to specific carbons and hydrogens in your final structure.
IR: strong, broad peak at 3400 cm-1
O-H stretch
MS: parent molecular ion at m/z = 122
Molecular weight is 122
C-13 NMR: peaks at 40, 60, 115, 120, 125, 140 ppm
4 different sp2 carbons ( labelled a below ),
2 different sp3 carbons ( b @ 40 ppm, c @ 60 ppm )
H-1 NMR:
d 2.0 ppm, 1H, broad singlet
b 2.7 ppm, 2H, triplet
c 3.6 ppm, 2H, triplet
a 7.0 ppm, 5H, broad multiplet