Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2005 |
Exam 1 Answer Key |
![]()
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2005 |
Exam 1 Answer Key |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown.
a) 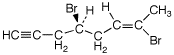
(S,Z)-4,7-dibromooct-6-en-1-yne
b) 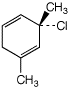
(S)-3-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-1,4-cyclohexadiene
c) ![]()
4-(3-cyclopentenyl)-3-butyn-1-ol
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for each of the following:
a) allyl fluoride
CH2=CH-CH2-F
b) vinyl chloride
CH2=CH-Cl
c) the HOMO of 1,3-butadiene (its orbital symmetry)
d) both enantiomers of 2,3-pentadiene
e) the enol of dimethyl ketone
3. (15 points) Complete the following reactions by adding the missing part(s): either the necessary reagents and conditions or the expected major product.
(6 pts) 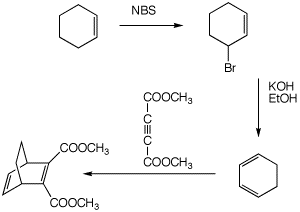
(6 pts) 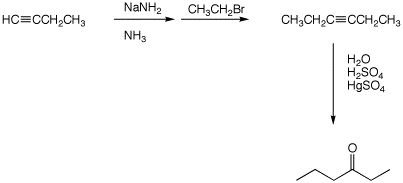
(3 pts) 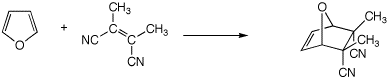
4. (16 points - 4 pts each)
a) Calculate the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency for a compound with the formula
C7 H11 Cl3 O2
and describe the significance of the result. Write at least one compound
consistent with the formula.
IHD = 1 , indicating a ring or double bond
lots of possible isomers, such as:
b) Draw a typical 1H NMR quartet and indicate the place(s) where the coupling constant (J) could be measured.
J could be measured as the spacing between any of the adjacent peaks
c) Butane gives a mass spectrum with major (m/z) peaks of 58, 57, 43,
29, and 15.
Identify the likely structures of each of those ions.
CH3CH2CH2CH3+. (m/z) = 58 (parent molecular ion)
CH3CH2CH2CH2+ (m/z) = 57 (could also be sec-butyl cation)
CH3CH2CH2+ (m/z) = 43 (could also be isopropyl cation)
CH3CH2+ (m/z) = 29
CH3+ (m/z) = 15
d) Predict the expected 13C NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene. Indicate the number of unique absorptions and their approximate chemical shifts.
6 different absorptions: CH3 (0-35 ppm), CH2 (15-40 ppm), aromatic (110-175 ppm)
5. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the addition of HCl to 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene.
Show the intermediates expected and all resonance forms.
There are two products
formed, A and B. A is the major product at low temperatures and B is
the major product at high temperatures.
Identify the structures
of A and B, and indicate which is the kinetic product and which is
the thermodynamic product.
Write a potential energy diagram that illustrates why the different products arise under different conditions.
(see page 407 in your text)
6. (19 points) Identify the unknown compound based on the following
information.
For each piece of information, indicate what you conclude about
the structure.
UV - no absorption above 200 nm
no pi bonds
IR - no absorptions in the range 3000 - 4000 cm-1
no O-H bonds, or C-H bonds on sp2 or sp carbons
no absorptions in the range 1600 - 2800 cm-1
no double or triple bonds
MS - molecular formula C6 H13 Br O
IHD = 0 (no rings or pi bonds)
major fragment appears at (m/z) 101
C6 H13 O - compound with Br removed (stable cation)
1-H NMR
a - 1.1 ppm, 3H, triplet
b - 1.7 ppm, 3H, singlet
c - 1.9 ppm, 2H, quartet
d - 3.3 ppm, 3H, singlet
e - 3.9 ppm, 2H, singlet