Organic Chemistry II
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2004 |
Final Exam Answers |
![]()
1. (25 points) Write a complete name for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown.
a) 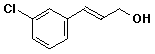
(E)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-propen-1-ol
b) 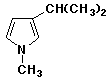
3-isopropyl-1-methylpyrrole
c) ![]()
(Z)-5-methoxy-4,6-heptadien-2-yn-1-ol
d) 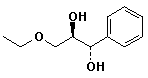
(1S,2R)-3-ethoxy-1-phenyl-1,2-propanediol
e) 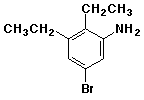
5-bromo-2,3-diethylaniline
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically indicated.
a) p-vinylbenzoic acid
b) 3-propoxypyridine
c) the HOMO of an allyl radical
d) (Z)-1,3-hexadiene-5-yne
e) the disulfide formed by oxidation of benzenethiol
3. (15 points) Write all resonance forms for the INITIAL
INTERMEDIATE formed in the following steps.
The arrow indicates the initial point of attack.
a) 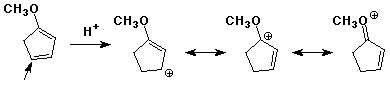
b) 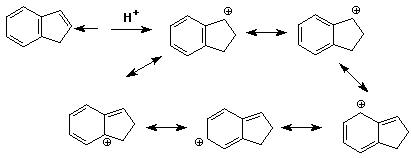
c) 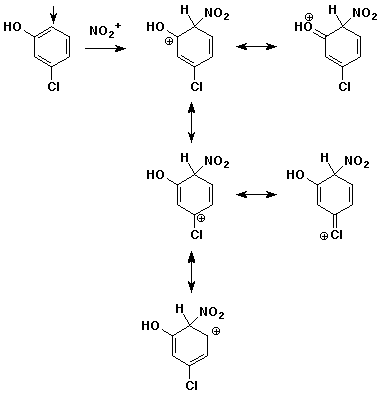
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Show stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 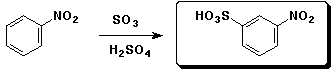
b) 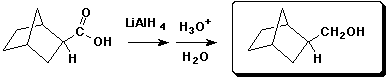
c) 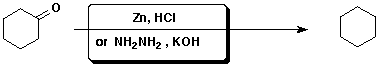
d) 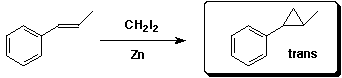
e) ![]()
5. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Show stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 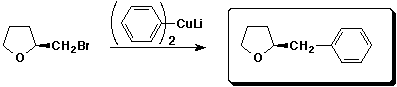
b) 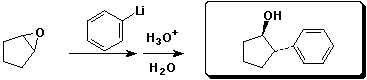
c) 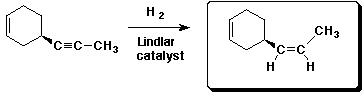
d) 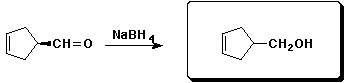
e) 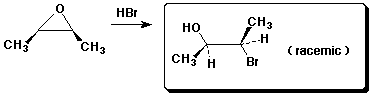
6. (20 points) Write synthetic sequences that could be used to prepare the following compounds.
a) you may begin with any alcohols having three carbons or fewer
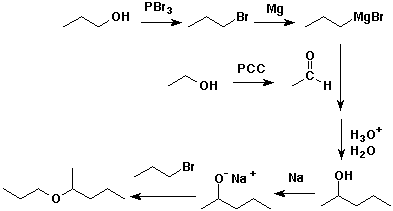
b) you may begin with benzene, acetylene, ethylene oxide, and any alcohols having three carbons or fewer
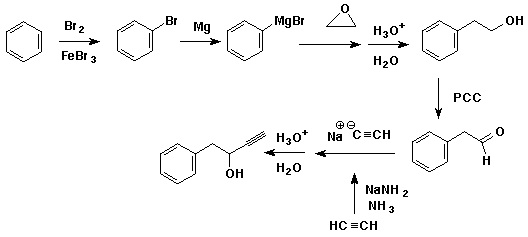
7. (15 points) Fill in the reagents that were likely used in the following synthetic sequence.
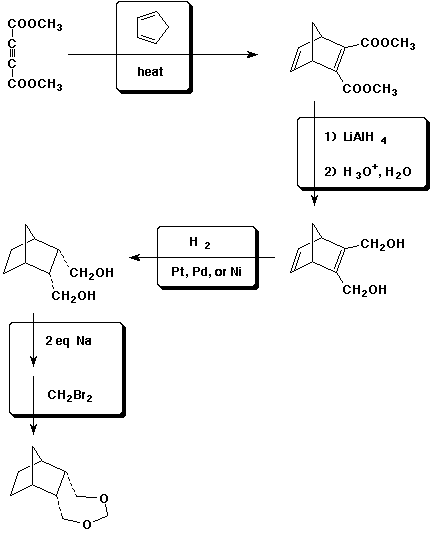
8. (15 points) Identify the unknown compound based on the information provided. For each item of information, indicate what structural information can be determined.
Molecular Formula C9 H18 O2
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency = 1
Infrared Spectrum
no peaks higher than 3000 cm-1 ( no sp or sp2 C-H, no O-H )
no peaks in the region 1600 - 1800 cm-1 ( no C=O or C=C )
H NMR Spectrum
a - 3.4 ppm, 4H, quartet
b - 2.1 ppm, 4H, triplet
c - 1.9 ppm, 6H, triplet
d - 1.1 ppm, 4H, triplet
d b - - a - c
9. (15 points) Identify the unknown compound based on the information provided. For each item of information, indicate what structural information can be determined.
Molecular Formula C12 H16 O2
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency = 5
Infrared Spectrum
no peaks higher than 3100 cm-1 ( no O-H )
several peaks in the region 2900 - 3100-1 ( both sp2 and sp3 C-H )
strong peak in the region 1700 - 1800 cm-1 ( C=O )
1H NMR Spectrum
a - 7-8 ppm, 5H, complex multiplet
b - 3.5 ppm, 2H, doublet
c - 2.7 ppm, 2H, singlet
d - 2.1 ppm, 1H, complex multiplet
e - 1.1 ppm, 6H, doublet
- a - - c - - - - b - d - e
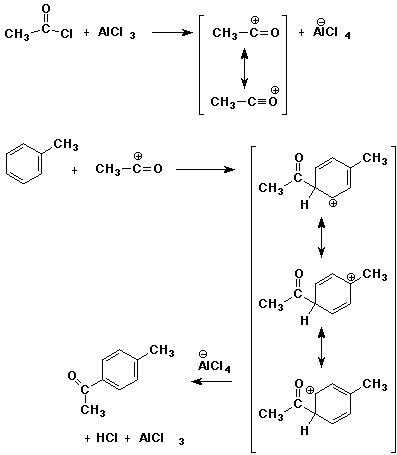
10. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the Friedel-Crafts
acylation shown below.
Show all steps and all resonance forms of any intermediates
involved.
Just show the pathway to the para product.
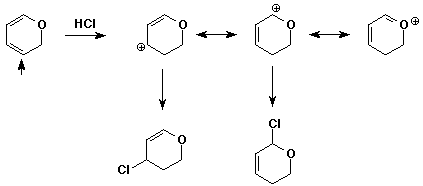
11. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the addition
reaction shown.
Predict the preferred site for the initial attack of H+.
Then show pathways to both 1,2 and 1,4 products, starting from the preferred
cation intermediate.
12. (15 points) Consider the reaction in which one equivalent of HBr adds to 1,3-butadiene.
Write a potential energy diagram, illustrating the relative energy levels of each of the species shown in the mechanism.
Explain how kinetic and thermodynamic control are illustrated in the diagram.
Kinetic control occurs at low temperature, when the lower Ea favors the less stable product.
Thermodynamic control occurs at higher temperatures, when the products are in equilibrium and the more stable product is favored.