Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2004 |
Exam 2 Answers |
![]()
Organic Chemistry II |
 |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chem 335 - Winter 2004 |
Exam 2 Answers |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown.
a) 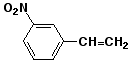
m-nitrostyrene or 3-nitrostyrene
b) 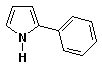
2-phenylpyrrole
c) 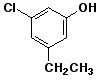
3-chloro-5-ethylphenol
d) 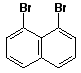
1,8-dibromonaphthalene
e) 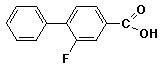
3-fluoro-4-phenylbenzoic acid
2. (15 points) Write all the resonance forms for the intermediate that would be formed in the indicated reactions. A final product or mechanism is not needed - just the resonance forms.
a) 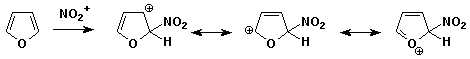
b) 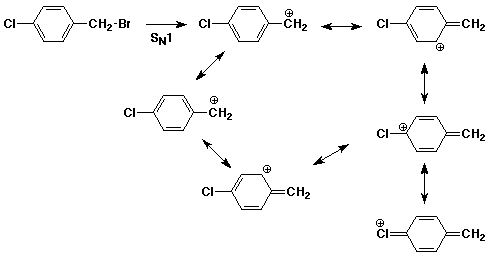
c) 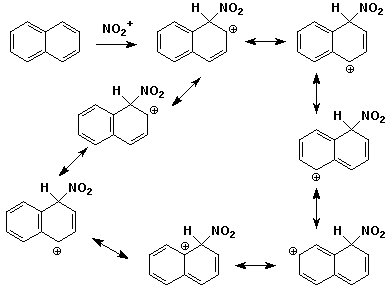
3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Show stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 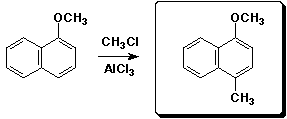
b) 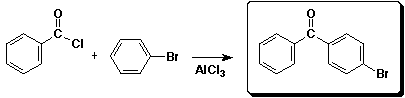
c) 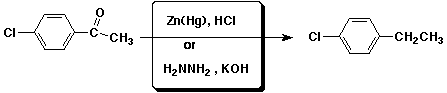
d) 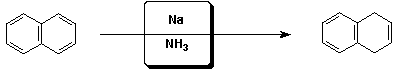
e) 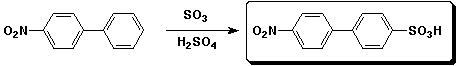
4. (20 points) Write synthetic sequences that could be used to prepare the following compounds.
a) (start with benzene, acetylene, and methane)
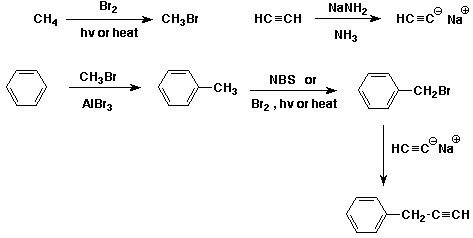
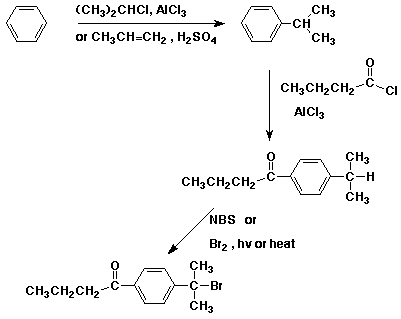
b) (start with benzene plus whatever other organic materials you need)
5. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the nitration of chlorobenzene. Show all steps and all resonance forms for the intermediate involved. Just show the pathway to the major product. Decide which will be the major product based on the partial rate factors for ortho (0.029), meta (0.0009), and para (0.137).

6. (10 points) The orbitals shown below represent the
HOMO and LUMO of a delocalized π system.
(HOMO = highest occupied
molecular orbital, LUMO = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital)
LUMO (top) / HOMO (bottom)
a) (2 pts) Label which is the HOMO and which is the LUMO.
b) (3 pts) Draw the structure of the compound for which
these are the HOMO and LUMO.
Is it a cation, neutral, or an anion?
(Note - there are five p orbitals and only 4 electrons - based on the HOMO)
c) (3 pts) Indicate the pattern of π energy levels for this
compound, including the number of electrons in each MO. Designate
which MOs are
the HOMO and LUMO in this diagram.
d) (2 pts) Draw the orbital symmetry for the lowest energy π molecular orbital.
7. (10 points) The pattern of molecular orbital energy levels shown below represents a delocalized π system.
LUMO (top) / HOMO (middle)
a) (2 pts) Label the HOMO and the LUMO on the diagram above.
b) (3 pts)
Draw the structure of the compound described by this pattern of MOs.
Is
it a cation, neutral, or an anion?
(Note - there are five p orbitals in a ring - based on the paired energy levels)
c) (3 pts) Is this compound aromatic? Explain, indicating each of
the criteria of Huckel’s Rule.
Yes.
It has 6 electrons (a 4n+2 number) in a planar,
continuous cyclic array of p orbitals.
d) (2 pts) Draw the orbital symmetry for the lowest energy π MO.