|
|
Organic Chemistry
II
|
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser
|
|
|
Chapter 14 Notes
|

Organometallics

Nomenclature
- organometallic implies a bond between a carbon and a metal
- named as alkylmetal, e.g., methyllithium or phenylmagnesium bromide
Structure and Bonding
- polar bond with negative carbon
- strongly basic and nucleophilic
Preparations
- from alkyl halides + active metal
- R-X + 2 Li --> R-Li + LiX
- R-X + Mg --> R-Mg-X
Reactions - Basicity
- pKa of corresponding conjugate acid (C-H bonds) very high (see table
in text)
- highly reactive with water and most other proton sources
- can be used to incorporate D by reaction with D2O
Grignard Syntheses
- Grignard reagents add a new C-C bond and make alcohols
- alkyllithium reagents react similarly, somewhat more reactive
- acetylide anions react similarly, making alkynols
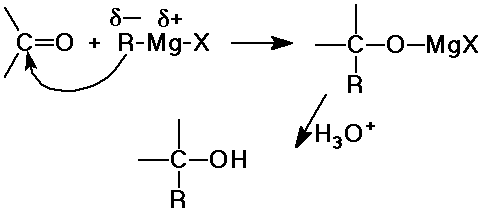
- Grignard + formaldehyde --> 1° alcohol
- Grignard + aldehyde --> 2° alcohol
- Grignard + ketone --> 3° alcohol
- Grignard (2 equiv) + ester --> 3° alcohol
- useful synthetic reaction
a new C-C bond is formed
builds up a larger carbon skeleton
- retrosynthetic analysis
- visualize carbon framework buildup by disconnections
- limitations: Grignard reagents are incompatible with most other polar
functional groups
(OH, COOH, NH2, etc.) and with atmospheric water and
oxygen
Coupling Reactions (Dialkylcuprates)
- preparation of Gilman reagents: 2 RLi + CuX --> R2CuLi + LiX
- coupling with alkyl halides: R2CuLi + R'X --> R-R'
+ RCu + LiX
- useful method for making larger alkanes from smaller pieces
- alkyl halide ( R' ) should be CH3 or 1° (SN2
reaction)
- alkyl cuprate ( R ) should be unhindered ( CH3 or
1° or aryl or vinyl )
Carbenes and Carbenoids
- carbene: divalent C with only 6 electrons (highly electron-deficient)
- carbenoid: carbene-like compound, usually with another molecule complexed
- alpha-elimination: removal of HX from the same carbon
- CHCl3 + KOtBu --> KCl + tBuOH + [ :CCl2 ]
( dichlorocarbene )
- dihalocarbene adds to a double bond to make a cyclopropane
- Simmons-Smith reaction
- CH2I2 + Zn --> I-CH2-Zn-I
(carbenoid)
- carbenoid adds CH2 to a double bond to
make a cyclopropane
Transition Metal Organometallics
- 18-electron rule
- equivalent of the octet rule for the transition metal series
(full shell, including d orbitals)
- ligand electrons surrounding the central metal ion total 18 for
best stability
- ligand exchange reactions can lead to catalysis of many reactions
- metallocenes
- "sandwich" compounds" with aromatic anion ligands
(e.g., cyclopentadienyl anion)
- Ziegler-Natta polymerization catalysts
- addition of substituted alkenes to make polyalkenes
- stereoregular polymers can be produced, e.g., isotactic polypropylene
![]()

![]()
![]()
