Organic Chemistry IProfessor
Carl C. Wamser |
|
 |
![]()
Exam 2 Answer Key
1. (25 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including stereochemistry.
a) 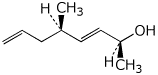
(2S,3E,5R)-5-methylocta-3,7-dien-2-ol
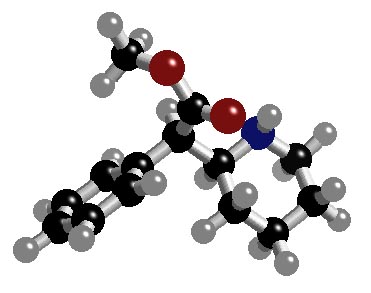
b) 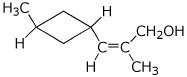
(Z)-2-methyl-3-(trans-3'-methylcyclobutyl)prop-2-en-1-ol
c) 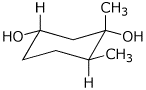
(1S,3S,6S)-1,6-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanediol
d) 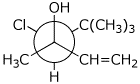
(3R,4S)-4-chloro-3,5,5-trimethylhex-1-en-3-ol
e) 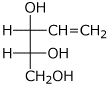
(2R,3R)-pent-4-en-1,2,3-triol
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) both enantiomers of 1-deuterioethanol

b) (R,R)-1,3-cyclopentanediol
![]()
c) the anti-Markovnikov addition product of HBr with 1-pentene
![]()
d) an isobutyl carbocation and what it would likely rearrange to
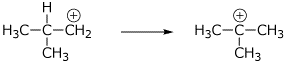
e) an SN2 transition state for NaOH plus (R)-2-bromobutane
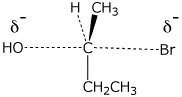
3. (15 points) Arrange each of the following in order with respect to the property indicated.
Write “MOST” under the compound with the highest value and “LEAST” under the compound with the lowest value.
a) stability
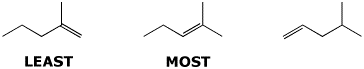
b) nucleophilicity
![]()
c) reactivity towards NaOH
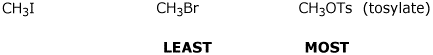
d) rate of dehydration
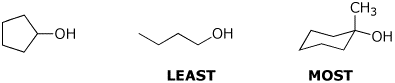
e) ratio of substitution over elimination
![]()
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the original starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Indicate stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 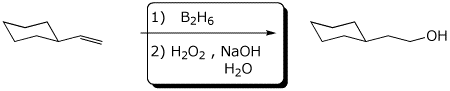
b) 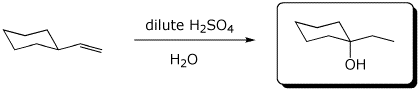
c) 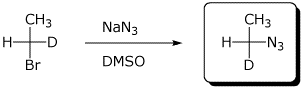
d) 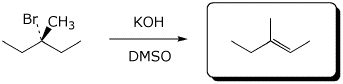
e) 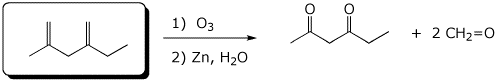
5. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the formation of the bromohydrin from propene. Show every step using electron-pushing arrows, particularly showing the expected regiochemistry and stereochemistry at every step.
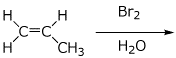
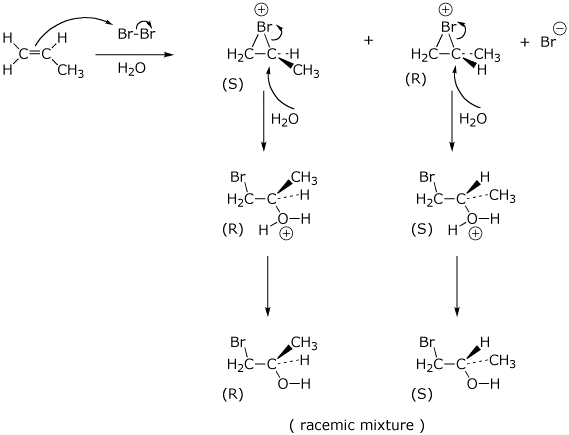
6. (15 points) (S)-3-Bromo-1,1-dimethylcyclopentane (shown below) is obtained in 100% optical purity. Upon heating in water, the product formed is 3,3-dimethylcyclopentanol, but only in 20% optical purity (inversion of stereochemistry predominates over retention).
Show the structures of the two stereoisomers of the product, indicate their absolute stereochemistry and identify which is the product of inversion and which the product of retention.
Based on the information given above, indicate the relative amounts of each stereoisomer formed, and give a mechanism that explains this result.
![]()