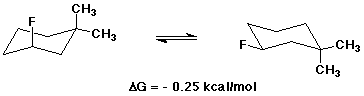1. (15 points) Write a complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds, including designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 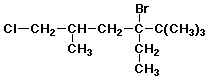
b) 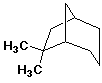
c) 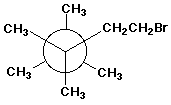
2. (15 points) Write clear structures that show the following:
a) the anti conformation of 1-bromopropane
b) isobutyl alcohol
c) a specific example of an alkane in which ALL hydrogens are primary
d) the cis and trans isomers of 1-chloro-3-methylcyclobutane
e) 2-methylspiro[3.4]octane
3. (10 points) The two compounds below are constitutional isomers, but upon losing a proton, they give the same anion. Write the two resonance forms for the resulting anion, and predict which will be the major contributor.
4. (15 points) Arrange each of the following in order with respect to the particular property indicated. Write MOST under the compound with the highest value or largest property and LEAST under the compound with the lowest value or smallest property.
a) acidity
![]()
b) boiling point
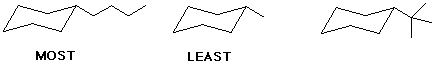
c) basicity
d) molecular dipole moment
e) acidity
![]()
5. (10 points)
(2 points each reaction) Complete each of the following acid-base
reactions.
(2 points each reaction) Use the table provided to decide the direction of each equilibrium. Write a large arrow indicating the preferred direction.
(2 points) Select EITHER ONE reaction and calculate the equilibrium constant Keq (or pKeq).
a) 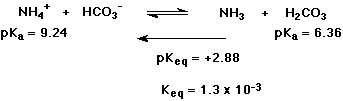
b) 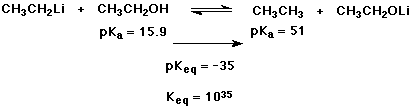
6. (10 points)
a) (3 points) What is the molecular formula for the compound below?
C8 H14 O2
b) (4 points) Identify the hybridization of every carbon.
c) (4 points) Identify all the primary hydrogens in the molecule.
7. (15 points)
(4 points each structure) Write Newman projections for all three
staggered forms of 2,3-dichloro-2,3-dimethylbutane, looking down
the C2-C3 bond.
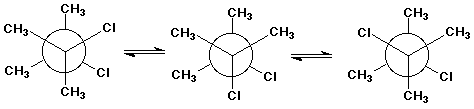
(3 points) You probably CANNOT predict which of the three conformations is the most stable. Explain what information you would need to know in order to make that prediction.
CH3 and CH3 , CH3 and Cl , Cl and Cl
8. (10 points) Write both chair conformations for 3-fluoro-1,1-dimethylcyclohexane.
Indicate which conformation is preferred, and use the table provided
to calculate delta G for the equilibrium between the two conformations.
Make sure that the sign of delta G is consistent with the direction
you wrote the equilibrium.