Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 2 Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 2 Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete names for each of the following.
a) 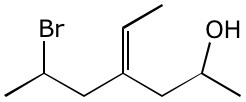
b) 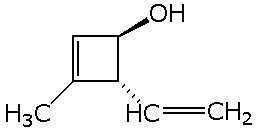
c) 
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) the epoxide from cis-2-pentene

b) allyl alcohol
![]()
c) the early transition state for reaction of an F atom with methane
![]()
d) sodium isobutoxide
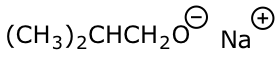
e) (Z)-2,4-dichloropent-3-en-1-ol
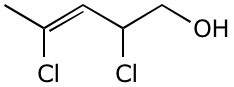
3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part:
either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product.
Show stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 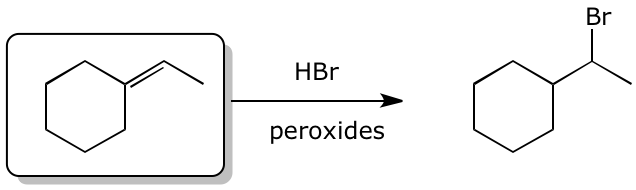
b) 
c) 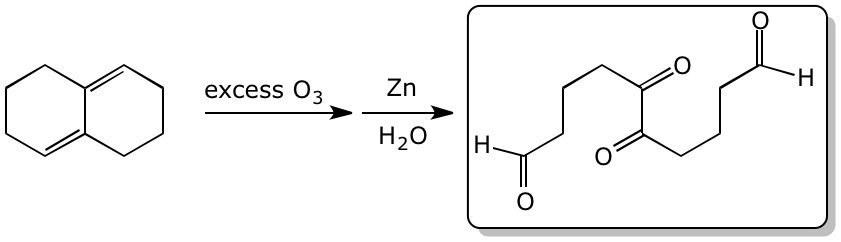
d) 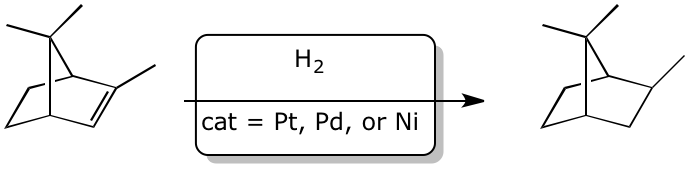
e) 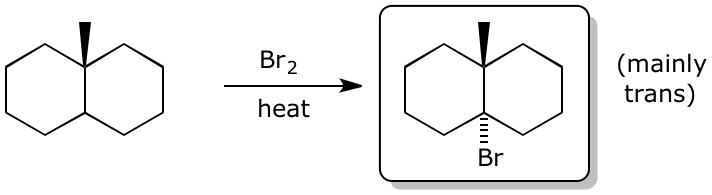
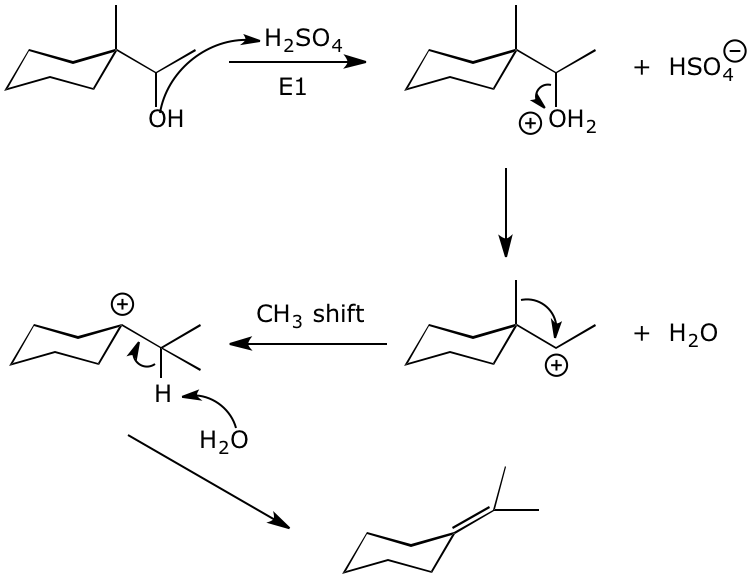
4. (15 points) Write complete mechanisms, including all steps and showing electron-pushing arrows, for the following reactions. Show the pathway to the expected major product in each case, being aware of possible rearrangements.

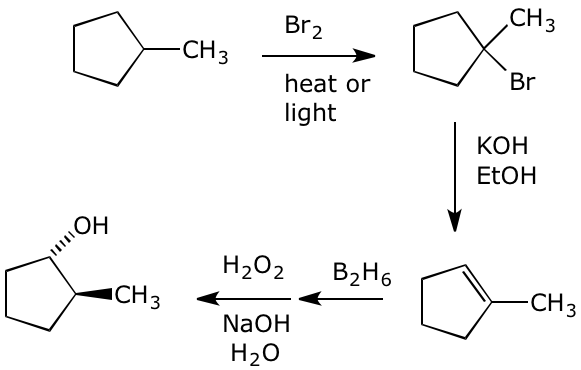
5. (10 points) Show a sequence of reactions that could be used to synthesize trans-2-methylcyclopentanol starting from methylcyclopentane. Just show the necessary reagents and conditions and products for each separate reaction. Mechanisms are not required.

6. (15 points) Consider whether hydrogen (H2) would be a suitable reducing agent for alkyl halides by calculating delta H for the reaction with all four of the possible methyl halides (CH3F, CH3Cl, CH3Br, and CH3I).
Which reactions are favorable? What else would you need to know to determine whether these reactions actually occur?
![]()

7. (14 points) When Br2 is added to an alkene and an additional nucleophile is provided, it is possible to add both to the double bond. For example, 1-methylcyclohexene reacts with bromine in the presence of excess sodium chloride to form a bromochloromethylcyclohexane, of which two possibilities are shown below.
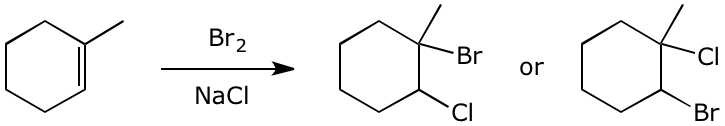
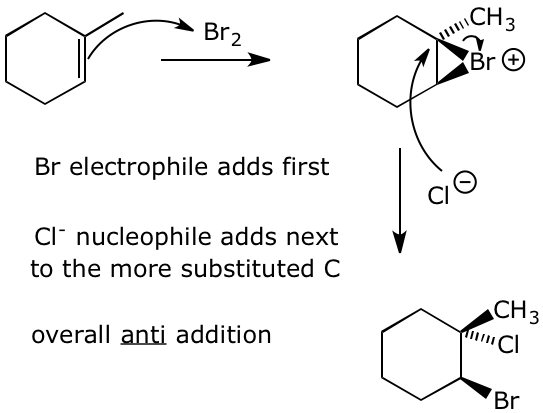
Predict which regiochemistry would be observed and also predict the most likely stereochemistry of the product. Write a complete mechanism to support your predictions.
![]()