Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 2 Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 2 Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete names for each of the following.
a) 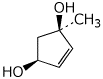
1-methylcyclopent-4-en-1,3-diol
(cis is a possible designation but it would be ambiguous in this case because there are two stereocenters)
b) 
(E)-5-bromo-8-methylnona-3,7-dien-2-ol
c)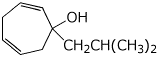
1-isobutylcyclohepta-2,5-dienol
1-(2-methylpropyl)cyclohepta-2,5-dienol
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) the initiation step in the photochlorination of butane
![]()
b) the epoxide from cyclobutene
![]()
c) the monomer repeat unit in Teflon
![]()
d) the transition state for SN2 substitution of ethanol by HI (include partial charges)
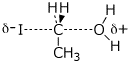
e) (E)-2-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-1-butene

3. (15 points) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write MOST and LEAST under the compounds with the highest and lowest values, respectively.
a) stability
![]()
MIDDLE / / / MOST / / / LEAST
b) reaction rate with bromine
![]()
LEAST / / / MOST / / / LEAST
(either option considered OK)
c) polarizability
![]()
MOST / / / MIDDLE / / / LEAST
d) C-X bond strength (not C-H)
![]()
LEAST / / / MIDDLE / / / MOST
e) rate of dehydration
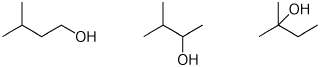
LEAST / / / MIDDLE / / / MOST
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Include stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 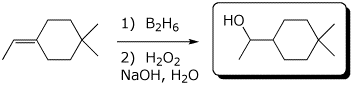
b) 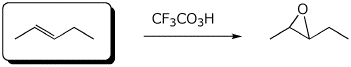
c) 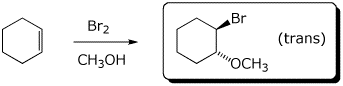
d) 
e) 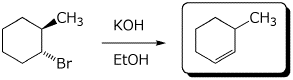
5. (10 points) Complete the following synthetic sequence by adding the missing parts in the empty boxes.

6. (15 points) A possible reaction of fluorine with ethane is shown below.
![]()
Rewrite the reaction to clearly show all the bonds broken and all the bonds made, and use the table of BDE values to calculate delta H for this reaction. Is this a favorable reaction?
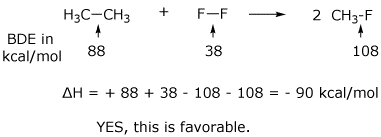
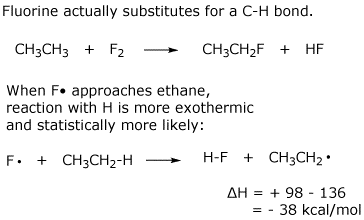
Write a logical chain mechanism to accomplish the above reaction, including a likely initiation step and two propagation steps. Calculate delta H for each step. Are all steps favorable reactions?

The major reaction of fluorine with ethane follows a different path. Predict what it would be and explain why it occurs in preference to the hypothetical reaction above.
7. (15 points) The alkene shown below can be isomerized with acid. Write a complete mechanism, including electron-pushing arrows.

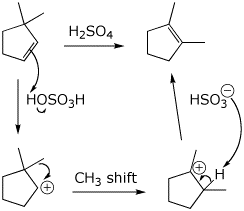
The same alkene reacts with bromine without any rearrangement. Write a complete mechanism and explain why there is no rearrangement in this mechanism.


![]()