Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 3 |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 3 |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
1. (20 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown.
a) 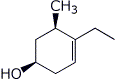
b) 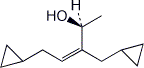
c) 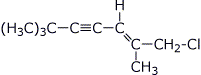
d) 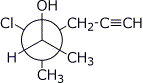
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) potassium tert-butoxide
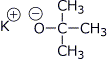
b) (S,S)-1,2-dimethylcyclobutane

c) the ozonolysis products from 2-butyne
![]()
d) a meso compound of formula C4H6Cl2Br2

e) a constitutional isomer of the meso compound you wrote immediately above, which is also a meso compound
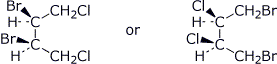
3. (10 points) Complete each of the structures on the right so that they represent the identical compound as the structure on the left. Clearly show every substituent on each chirality center.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) Describe the relationship between compounds (a) and (c).
They are enantiomers.
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Show stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 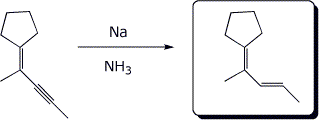
b) 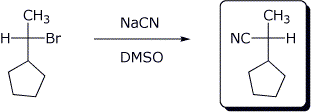
c) 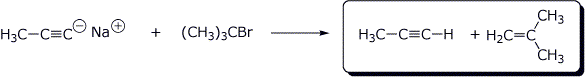
d) 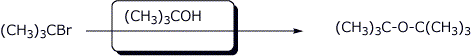
e) 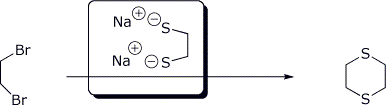
5. (10 points) Show the sequence of reactions that would be used to synthesize trans-2-pentene, starting with acetylene and any alkyl halides having two or fewer carbons.
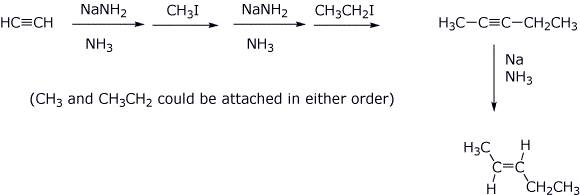
6. (15 points) Carefully follow the stereochemistry of addition (anti) of Br2 to trans-2-pentene. Show the stereochemistry (with R and S designations) of the intermediates that are possible, as well as all the stereoisomeric products that are possible from the anti addition mechanism.

7. (15 points) A chem student wanted to prepare the chiral alkyne shown below. Show the structure (with stereochemistry) of the alkyl halide she should choose to get the desired stereochemistry of the product.

The desired product has the formula C6H10 , but the only products that could be isolated had formulas of C2H2 or C4H8. Keeping in mind that acetylides are strong bases as well as good nucleophiles, explain what went wrong with the synthesis, and give structures for the products of formula C2H2 (one isomer) and C4H8 (three isomers).

![]()