|
|
Organic Chemistry I |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Exam 3 |
![]()
|
|
Organic Chemistry I |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Exam 3 |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete names for each of the following.
a) 
b) 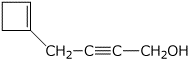
c) 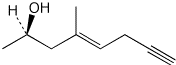
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) two diastereomers of 2,3-dichlorobutane
b) two enantiomers of 2,3-dichlorobutane
c) ozonolysis products from 2-pentyne
d) (R,R)-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
e) the transition state for an SN2 reaction of I- with isobutyl bromide
3. (15 points) Arrange each of the following in
order with respect to the property indicated.
Write “MOST” under the compound with the highest value and “LEAST” under
the compound with the lowest value.
a) nucleophilicity
CH3ONa / / CH3COONa / / CH3COOH
b) reactivity in an SN2 mechanism
1-bromobutane / / 2-bromobutane / / 2-chlorobutane
c) reactivity towards methyl iodide
NaCl in EtOH / / NaCl in DMSO / / EtOH
d) acidity
cyclobutane / / 1-butene / / 1-butyne
e) ratio of substitution/elimination using NaOEt in EtOH
n-butyl bromide / / sec-butyl bromide / / tert-butyl bromide
4. (15 points) Complete the following reactions
by indicating the major product expected.
Show stereochemistry
if it
is specific.
If the reaction can be described as
SN1, SN2, E1, or E2, indicate that.
a) 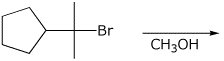
b)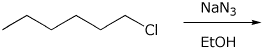
c) 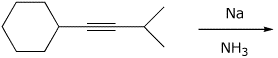
d) 
e) 
5. (15 points) Complete the following structures so as to show both enantiomers of trans-1,3-dichlorocyclohexane in both of their chair conformations. Place the Cl substituents on the positions marked with the dots.
Identify each stereocenter as R or S on EVERY structure.
Identify which conformation is the more stable one for each enantiomer.
6. (10 points) Preparation of 2,3-dibromobutane from 2-butyne can be done
by addition of one equivalent of Br2 and one equivalent of H2.
Does it matter whether the order of addition was reversed?
Illustrate the
process for a syn addition of one equivalent of H2 followed
by an anti addition of Br2.
7. (15 points) Show how you could prepare butane, starting from acetylene as your ONLY source of carbon.