|
|
Organic Chemistry I |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chapter 8 Notes |
![]()
|
|
Organic Chemistry I |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Chapter 8 Notes |
![]()
![]()
Recognizing Nucleophiles
Solvents
The SN2 Mechanism
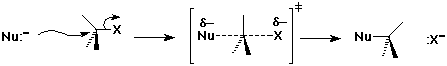
SN2 Mechanism - Evidence
SN2 Mechanism - Evidence
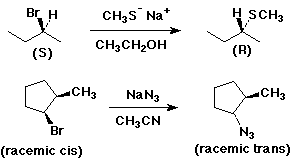
SN2 Mechanism - R Groups
![]()
SN2 Mechanism - X Groups
SN2 Mechanism - Nucleophiles
Solvent Effects on Nucleophilicity
SN1 Mechanism
SN1 Mechanism - Evidence
SN1 Mechanism - Evidence
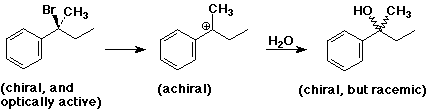
SN1 Mechanism - R Groups
SN1 Mechanism - X Groups
Solvolysis Reactions
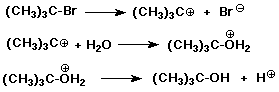
Neighboring Group Effects - Mustard Gases
Phase-Transfer Catalysis
Beta-Elimination Reactions
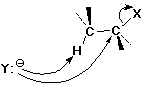
E2 Elimination Mechanism
E2 Stereochemistry
Zaitsev Rule
E1 Elimination Mechanism
Substitution or Elimination ?
Nucleophile or Base?
Reactivity Patterns
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(steric hindrance) |
(carbocation stability) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
weak base |
|
weak nucl. |
|
|
no base, good nucl. |
weak base |
weak base, poor nucl. |
|
|
|
poor base |
|
weak base, poor nucl. |
|
|
strong base, e.g., OH- |
weak base, e.g., I- |
strong base, e.g., tBuO- |
weak base, e.g., H2O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]()