|
|
Organic Chemistry I |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Exam 2 Answer Key |
![]()
|
|
Organic Chemistry I |
|
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
||
Exam 2 Answer Key |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown.
a) 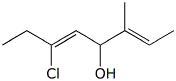
(2E,5Z)-6-chloro-3-methyl-2,5-octadien-4-ol
b) ![]()
trans-4-vinylcyclohexanol
or
trans-4-ethenylcyclohexanol
c) 
5,5-dimethyl-6-hepten-1,4-diol
2. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Show stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 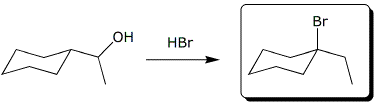
b) 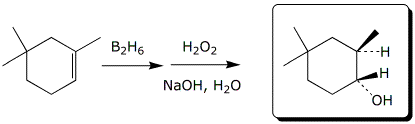
c) 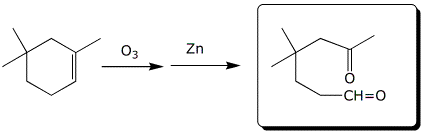
d) 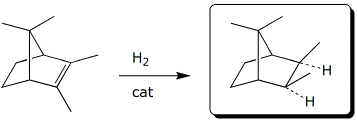
e) 
3. (15 points) Show a sequence of reactions that could be used to prepare the target compounds, starting from the original compound.
a) 3-ethyl-2-pentene, starting from 3-ethylpentane
b) 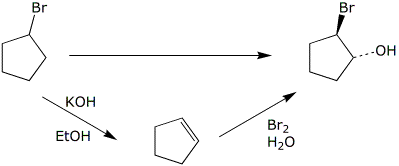
c) 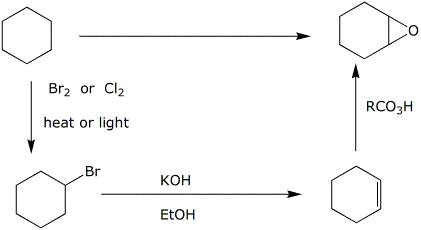
4. (15 points) The same two products arise, in the same ratio, from acid-catalyzed hydration of either 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene or 1,6-dimethylcyclohexene. Identify the two products by writing accurate structures for each. Predict which product will be the major product by referring to the mechanism.
Both alkenes give the same tertiary carbocation upon protonation.
Addition of the nucleophile is preferred from the side opposite the adjacent methyl group.
5. (10 points) Write a complete mechanism for the dehydration of 3-methyl-2-butanol using hot aqueous sulfuric acid. Show all steps and use electron-pushing arrows. Show the pathways to all likely products.
6. (15 points) The anti-Markovnikov addition of HBr to alkenes works as a chain reaction because both propagation steps are energetically favorable. Write out the two propagation steps for the overall reaction shown below. Use the bond dissociation energies shown below to calculate ΔH for each step and for the overall reaction.
7. (15 points) The conversion of 2-butanol to 2-iodobutane by HI could conceivably go by an SN1 or an SN2 mechanism. Write a complete mechanism for each case, showing all steps and using electron-pushing arrows. Also write clear potential energy diagrams for each case, labeling each step with the corresponding structure.
![]()