Functional groups
alkyl halide: R-X (X = halogen atom)
alcohol: R-O-H (hydroxyl group)
Functional Group Classification
- based on the carbon the X or OH group is attached to:
1° , 2° , 3°
- ethyl alcohol
CH3CH2OH (1°)
- isopropyl chloride
(CH3)2CHCl (2°)
- t-butyl alcohol
(CH3)3COH (3°)
Alkyl Halide Nomenclature
- halogen substituents are indicated by the prefixes fluoro-, chloro-,
bromo-, and iodo- and listed in alphabetical order with other substituents
- common names - name the alkyl group followed by the name of the halide
e.g., methyl chloride or chloromethane
- several polyhaloalkanes are common solvents and are generally referred
to by their common names
e.g., chloroform or trichloromethane, Freon 12 or dichlorodifluoromethane
- hydrocarbons in which all hydrogens are replaced by halogens are commonly
named as perhaloalkanes
e.g., perfluoroethane or 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexafluoroethane
Alcohol Nomenclature
- common name: alkyl alcohol
- IUPAC: alkanol
- OH group takes priority over substituents
- it must be in the parent chain
- the direction of numbering gives it the lower possible number (regardless
of substituents)
- use -ol suffix with number designation
- name other substituents as prefixes as usual
- more than one alcohol named as a -diol, -triol, etc.
Alcohol Examples
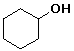
cyclohexyl alcohol or cyclohexanol
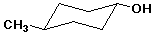
trans-4-methylcyclohexanol
Structure of Alcohols
- sp3 O with two covalent bonds and two lone pairs
- The bond angle about oxygen is about 105°, explained as greater
repulsions of the lone pairs towards the bonding pairs
Boiling Points of Alkyl Halides
- among constitutional isomers, branched isomers have a more compact
shape, decreased area of contact, decreased van der Waals attractive
forces between neighbors, and lower boiling points
- 1-bromobutane (n-butyl bromide) bp = 100°
- 2-bromo-2-methylpropane (t-butyl bromide) bp = 72°
- for an alkane and an alkyl halide of comparable size and shape, the
alkyl halide has the higher boiling point
the difference is due almost entirely to the greater polarizability of the
three unshared pairs of electrons on halogen compared with the polarizability
of shared electron pairs of the hydrocarbon
- ethane bp = -89°
- bromomethane bp = 4°
- boiling points of alkyl fluorides are lower than those of hydrocarbons
of comparable molecular weight
the difference is due to the small size of fluorine, the tightness with which
its electrons are held, and their particularly low polarizability
- 2-methylpropane bp = - 1°
- 2-fluoropropane bp = - 11°
Polarity of Alkyl Halides
- dipole moment of RX depends on:
the sizes of the partial charges,
the distance between them, and
the polarizability of the unshared electrons on halogen
- dipole moments of all the haloalkanes are comparable
Hydrogen Bonding
- attraction between the positive end of one dipole (an H bonded to F,
O, or N - atoms of high electronegativity) and the negative end of a
dipole, usually a lone pair on F, O, or N
- in alcohols, O lone pairs interact with polar H bonds
- covalent O-H bond strength ~ 100 kcal/mole
- O...H (H-bond) strength ~ 5 kcal/mole
Effects of H-Bonding
- alcohols have higher boiling points than alkanes (nonpolar) or alkyl
halides (polar, but no H-bonds)
- ethers are polar but have no H-bonds
(pentane and diethyl ether both boil at about 35°, but 1-butanol has
a bp of 117°)
- H-bonds hold together the strands of DNA ("Velcro" effect)
- H-bonding increases water solubility
Acid-Base Reactions of Alcohols
- remember analogy with water
- reactions as bases:
H2O + H+ <==> H3O+
ROH + H+ <==> ROH2+ (an oxonium ion)
- reactions as acids:
H2O + B- <==> B-H + OH-
ROH + B- <==> B-H + RO- (an alkoxide ion)
Mechanism of Proton Transfer - Potential energy diagram
- potential energy (delta H or delta G) vs reaction progress (or reaction
coordinate)
- features of a typical potential energy diagram: transition state, delta
H, Ea
Acidity of Alcohols
- alcohols about as acidic as water
MeOH more acidic, EtOH less acidic
3° alcohols much weaker acids
- pKa values: 3° > 2° > 1° > MeOH
18 , 17, 16, 15.5 (compare H2O: pKa = 15.7)
- tBuOH + NaOH ---> unfavorable
Substitution Reactions with HX - SN1 Mechanism
- halide substitution by a three-step (SN1) mechanism
tBuOH + HBr --> tBuOH2+ --> tBu+ --> tBuBr
- acid-base reaction sets up H2O as a good leaving
group
- carbocation (3°) intermediate
- Br- as a nucleophile
- potential energy diagram
- rate-determining step is formation of the carbocation
Carbocations
- structure: trivalent sp2 C with only 6 electrons (electron-deficient)
- stability order: favored by electron donation by substituents
3° > 2° > 1°
Reactivity
- alcohol reactivity parallels carbocation stability: 3° > 2° > 1°
- more stable intermediate (carbocation) implies a lower Ea (more stable
transition state)
Hammond's Postulate
- What does a transition state look like?
- a transition state looks like something between reactants and
products
but closer in structure to whichever it is closer in energy to
- Hammond's Postulate: the structure of the transition state
for an exothermic reaction looks more like the reactants of that step
for an endothermic reaction looks more like the products of that step
- for the SN1 substitution, the rate-determining step is formation of
the carbocation (endothermic)
- transition states look mainly like a carbocation (and are more stable
if the carbocation is more stable)
Substitution Reactions with HX - SN2 Mechanism
- 1° and methyl alcohols don't form stable carbocations, don't do
SN1 well
MeOH + HBr --> MeOH2+ Br- --> MeBr + H2O
concerted displacement of H2O by Br- (bimolecular)
Halogen Substitution with Other Reagents
- PBr3 + alcohol gives alkyl bromide, with less
rearrangement than with HBr
- SOCl2 + alcohol gives alkyl chloride, also with
less rearrangement
Halogenation of Alkanes

Free Radicals
- radical: any chemical species that contains one or more unpaired electrons
- radicals are formed by homolytic cleavage of a bond
- a barbed curved (fishhook) arrow is used to show the change in position
of a single electron
- the order of stability of alkyl radicals is 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3
- radical initiators like peroxides (ROOR) have weak bonds, eaily broken
Mechanism - Chain initiation
- a step in a radical chain reaction characterized by formation of radicals
from nonradical compounds
Mechanism - Chain propagation
- a step in a radical chain reaction characterized by reaction of a radical
and a molecule to form a new radical
- Cl. + CH3CH3 --> CH3CH2. + HCl
- CH3CH2. + Cl2 --> CH3CH2Cl + Cl.
- notice that the radicals recycle
- chain length, n: the number of times the cycle of chain propagation
steps repeats in a chain reaction
Mechanism - Chain termination
- a step in a radical chain reaction that involves destruction of radicals
- 2 Cl. --> Cl2
- CH3CH2. + Cl. --> CH3CH2Cl
- 2 CH3CH2. --> CH3CH2CH2CH3
Energetics
- using BDE data, calculate the heat of reaction, delta H°, for the
halogenation of an alkane
- delta H = sum of bonds broken - sum of bonds made
Halogenation of Larger Alkanes
- regioselectivity of 2° hydrogen over a 1° hydrogen is high
for bromination
- propane + Br2 --> 1-bromopropane (8%) + 2-bromopropane (92%)
- regioselectivity is not as high for chlorination
- propane + Cl2 --> 1-chloropropane (43%) + 2-chloropropane
(57%)
- regioselectivity is 3° > 2° > 1°
for bromination - approximately 1600:80:1
for chlorination - approximately 5:4:1
- predict products based on regioselectivity (energetic factor) x statistical
factor (number of H's)
- example: draw all monobromination products for isobutane and predict
the % of each for a given reaction
Regioselectivity
- the regioselectivity of chlorination and bromination
can be accounted for in terms of the
relative stabilities of alkyl radicals (3° > 2° > 1° > methyl)
- how do we account for the greater regioselectivity of
bromination (1600:80:1) compared with chlorination (5:4:1)?
Hammond's Postulate
- in halogenation of an alkane, the rate-limiting step is hydrogen abstraction
this step is exothermic for chlorination and endothermic for bromination
- because hydrogen abstraction for chlorination is exothermic,
the transition state resembles the alkane and a chlorine atom,
there is little radical character on carbon in the transition state, and
regioselectivity is only slightly influenced by radical stability
- because hydrogen abstraction for bromination is endothermic,
the transition state resembles an alkyl radical and HBr,
there is significant radical character on carbon in the transition state,
and
regioselectivity is greatly influenced by radical stability.
Radical stability
- 3° > 2° > 1° > methyl
- 3° C-H bond 91 kca/mol
- 2° C-H bond 95 kca/mol
- 1° C-H bond 98 kca/mol
- regioselectivity is in the same order
- the order is like carbocation stability and for a similar reason -
the radical center is electron-deficient and needs electron donation
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()