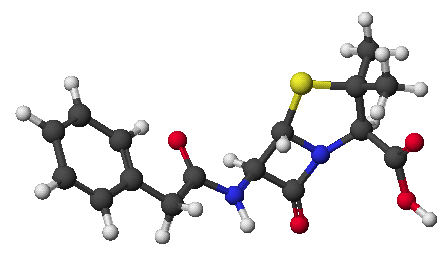
Chem 334 - Fall 2001
Organic Chemistry I
Dr. Carl C. Wamser

1. (25 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 
(Z)-5-chloro-4-hepten-1-ol
b) 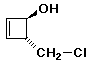
(1R,4R)-4-(chloromethyl)-2-cyclobutenol
c) 
(1R,2S)-1-bromo-2-chloro-1-cyclopentyl-4,4-dimethylpentane
d) 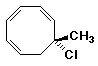
(R)-7-chloro-7-methyl-1,3,5-cyclooctatriene
e) 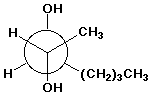
(2S,3S)-2,3-heptanediol
2. (20 points) Examine the pairs of structures below and identify their relationship to one another, using the letter codes below:
A - the identical structure
B - constitutional isomers
C - conformational isomers
D - diastereomers
E - enantiomers
F - none of the above
a) 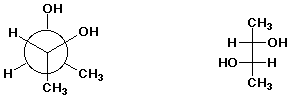 D
D
b)  B
B
c)  D
D
d) 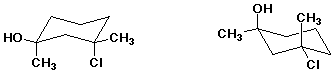 C
C
e)  E
E
3. (20 points) Arrange the following sets of compounds in order with respect to the property indicated. Write "MOST" and "LEAST" under the compounds with the highest and lowest values of the property.
a) stability
![]()
LEAST / / MOST / / MIDDLE
b) stability
![]()
MIDDLE / / MOST / / LEAST
c) basicity
![]()
LEAST / / MIDDLE / / MOST
d) rate of hydrolysis in neutral water solution
![]()
MIDDLE / / MOST / / LEAST
e) rate of reaction with bromine

LEAST / / MIDDLE / / MOST
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part - either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Show stereochemistry if it would be specific.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 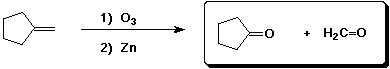
e) 
5. (20 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the expected major product. Show stereochemistry if it would be specific. Also indicate the most likely mechanism: E1, E2, SN1, or SN2.
a) 
b) 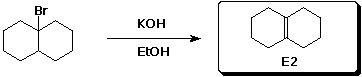
c) 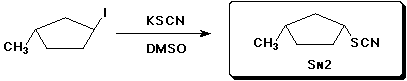
d) 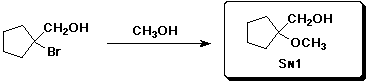
e) 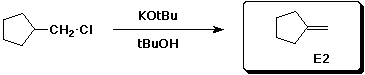
6. (20 points) Show a sequence of reactions that could be
used to accomplish each of the following conversions.
(Just show the individual reactions and products from each step
- no mechanisms are required.)
a) 
b) 
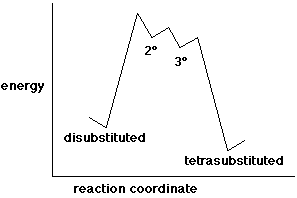
7. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed isomerization shown below. Write all steps and show electron-pushing arrows.
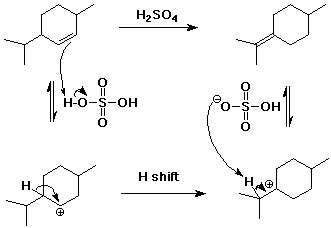
Write an approximate potential energy diagram. Carefully show the relative energy levels of the reactant and product and any intermediates.
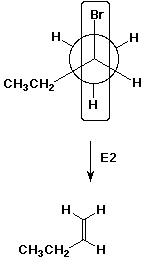
8. (20 points) Write Newman projections for all three staggered conformations of (R)-2-bromobutane, viewing down the C2-C3 bond.

Upon treatment with strong base (e.g., OH- ), three alkene isomers are formed. Illustrate which of the above conformations would be expected to lead to cis or trans 2-butene. Predict which will be the major product and explain why.
Trans-2-butene is the major product. It comes from the more stable conformation of the original compound.
Write a Newman diagram that would illustrate the conformation that would be needed to generate 1-butene.
9. (20 points) Polypropylene is prepared from the monomer propene (common name propylene). Illustrate a typical propagation step in the free radical chain reaction that makes polypropylene.
![]()
Polypropylene has a methyl group on every alternate carbon
of the polymer chain, which is a result of the regiochemistry
of each addition step.
Explain what regiochemistry means and why this particular regiochemistry
is observed.
Regiochemistry refers to the orientation of addition to a double bond (in this case). The addition follows a Markovnikov-type pattern in which the radical adds to the pi bond so as to generate the more stable new radical (secondary rather than primary).
This preference for addition happens at every step, so the methyl groups appear regularly on alternate positions.
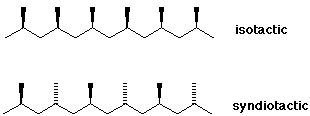
Depending on the exact conditions of synthesis, polypropylene can exhibit different stereochemical possibilities at each of the stereocenters along the polymer chain. Describe the stereochemical possibilities.
The tertiary carbons in the chain are stereocenters, which can be oriented relatively all the same (isotactic), alternating (syndiotactic), or random (atactic).
10. (20 points) In the process of breaking down glucose to extract energy, the enzyme aconitase catalyzes the isomerization of citric acid to isocitric acid.

Citric acid is achiral. Explain.
Citric acid has no stereocenters.
Isocitric acid is chiral. Identify the absolute configuration of all stereocenters in isocitric acid. (Label them on the above structure).
2R,3S
The isomerization mechanism involves initial dehydration to form a compound with a (Z) double bond. Write its structure.

The second stage of the mechanism involves hydration of the (Z) double bond to form isocitric acid. Illustrate and give the appropriate name for the specific stereochemistry of this reaction.
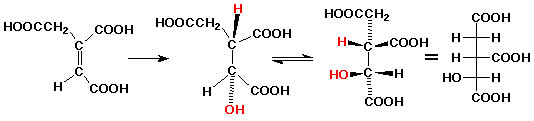
This is an anti addition.