Chem 334 - Fall 2001
Organic Chemistry I
Dr. Carl C. Wamser

1. (20 points) Write complete names for each of the following, including stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 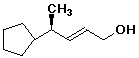
b) 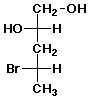
c) 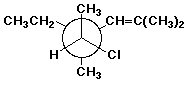
d) 
2. (15 points) Examine the pairs of structures below and identify their relationship to one another, using the letter codes below:
A - the identical structure
B - constitutional isomers
C - conformational isomers
D - diastereomers
E - enantiomers
F - none of the above
a) ![]()
b) 
c) 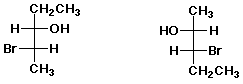
d) 
e) 
3. (15 points) Arrange the following sets of compounds in order with respect to the property indicated. Write "MOST" and "LEAST" under the compounds with the highest and lowest values of the property.
a) nucleophilicity
![]()
b) reactivity in an SN2 reaction
![]()
c) reactivity in an SN1 reaction

d) ratio of substitution / elimination with 1-bromopropane
![]()
e) rate of reaction with NaI in acetone
![]()
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions
by adding the missing part - either the starting compound, the
necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product.
Show stereochemistry if it would be specific.
If the mechanism could be classified as SN1,
SN2, E1 or E2, indicate that.
a) ![]()
b) ![]()
c) 
d) 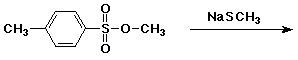
e) 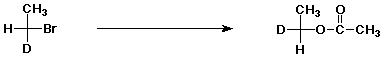
5. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the solvolysis
of 2-bromo-3-methylbutane in methanol.
Write all steps and show electron-pushing arrows.
Show pathways to ALL possible products, including rearranged and
unrearranged products, both substitution and elimination.
6. (20 points) Consider the addition of bromine to 3-methylcyclopentene
to form 1,2-dibromo-3-methylcyclopentane.
First write the balanced reaction WITHOUT stereochemistry.
(4)
Note that the product has three stereocenters.
Starting with (S)-3-methylcyclopentene, ONLY TWO stereoisomeric
products are formed. Write their structures, determine absolute
configurations at every stereocenter, and describe their relationship.
(8)
Show a complete mechanism, clearly following the electron-pushing
and the stereochemistry at each step. Make sure your mechanism
shows pathways to both products. Predict whether the products
should be formed in equal amounts, or whether one is favored.
Explain.
(8)