If a bird doesn't sing, I'll make her SING.
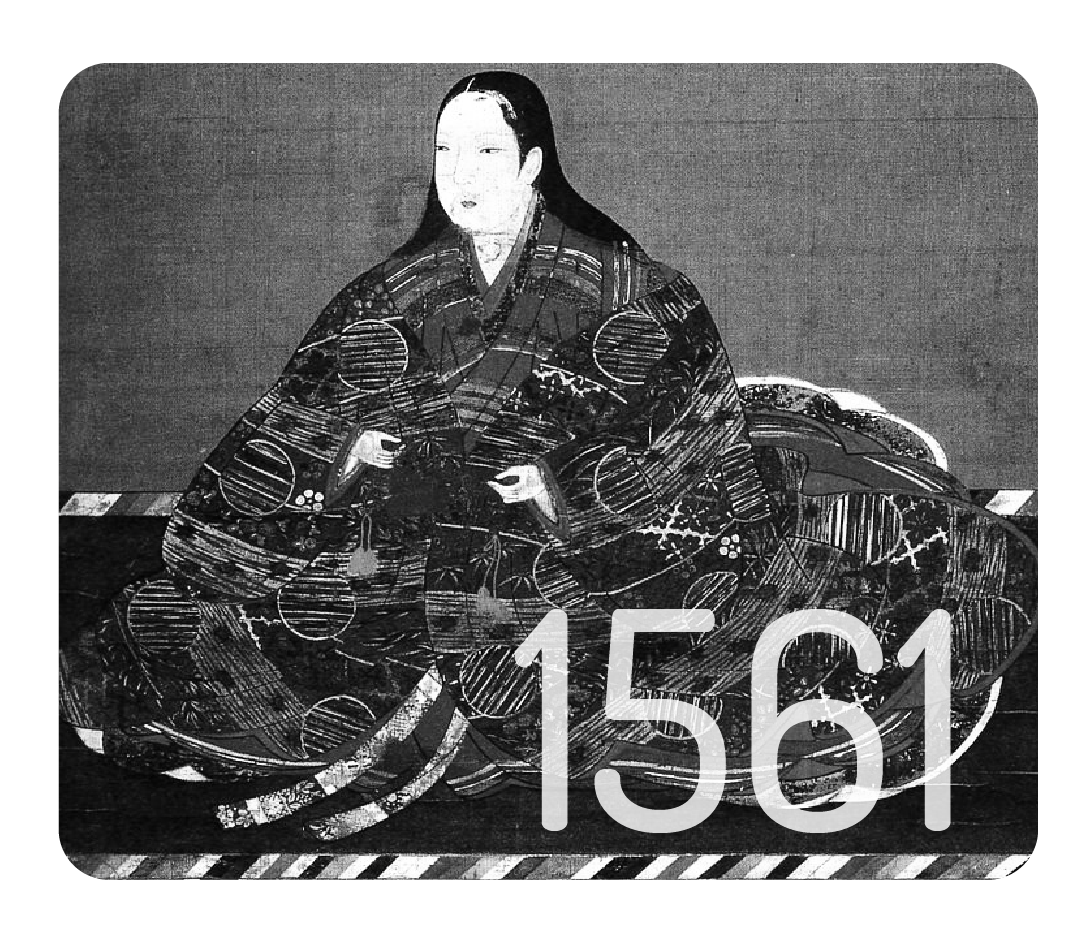













Toyotomi Hideyoshi (March 17, 1537 – September 18, 1598) was a preeminent daimyō, warrior, general, samurai, and politician of the Sengoku period who is regarded as Japan's second "great unifier". He succeeded his former liege lord, Oda Nobunaga, and brought an end to the Warring Lords period. The period of his rule is often called the Momoyama period, named after Hideyoshi's castle. After his death, his young son Hideyori was displaced by Tokugawa Ieyasu.









