Chem 221
Lecture 21- 11/12
Electron Density Distributions
Ions vs Neutral Atoms
Li vs Li+
- What two effects important?

Be vs Be2+
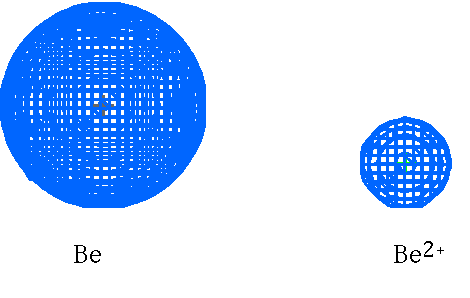
Be2+ vs Li +

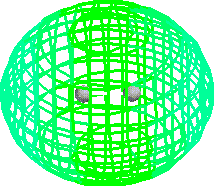
Isodensity Surfaces:
Connect all points with a particular value of electron density
- Molecule Size: density = 0.002 electrons/Å.
LiH H2 HF
- Electron cloud about H?
- HF: acting like H+ (hydrogen ion)
- LiH: acting like H- (hydride)


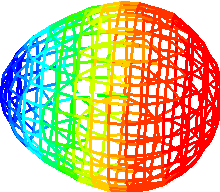
Higher electron density surfaces
Li
LiH H2 HF


Fluorine wants electrons more than H
Electron density concentrated around H
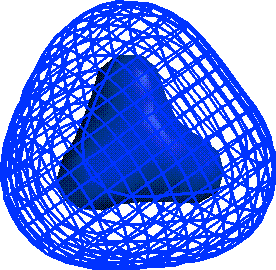
Electrostatic Potentials
Simplify electrostatic information:
- Use colors:
- most repulsive region: red (negative)
- most attractive region: blue (positive)
LiH H2 HF
What does the model show:
LiH: Li blue, H red
charge separation
equal distribution of density
Fluorine negative - hugging electrons
Conclusion?
- LiH: electrostatic attraction - ionic bonding
- H2: shared electrons - covalent bonding
- HF: somewhere between - polar covalent
Ionic vs Covalent:
CH4 NaCl H2CO KF
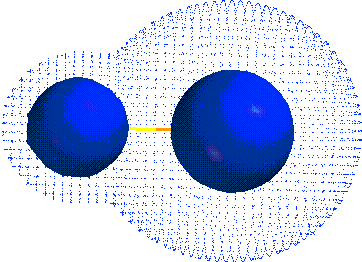
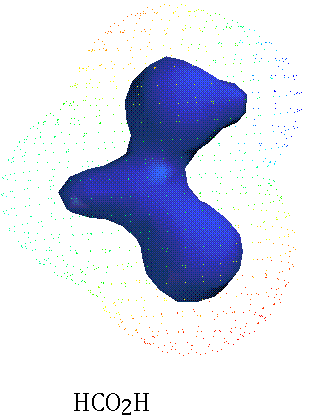
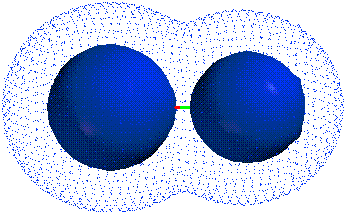
ELECTRONEGATIVITY:
Scale that gives a measure of how much atom wants
e-
H2O CO2
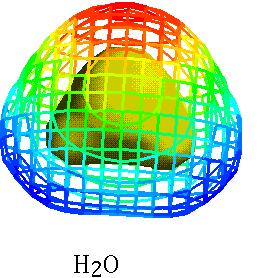
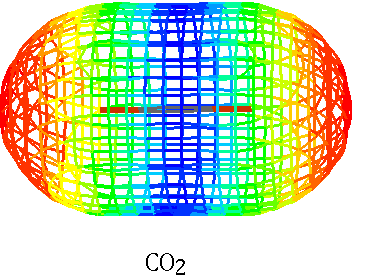
Electrons shared unequally
- Where is the negative end of the molecule?
Structure and Polarity
Electric dipole:
- Dipole allows us to quantify the charge separation
- One has NET DIPOLE, which one?
- Water has a dipole moment !
- What do we know about polar and non polar substances?
Polarity
This is illustrated with chromatography
- Separation is based on interactions
- between substance and paper
- between substance and solvent
·Simplify by looking only at solvents:
- H2O and ethyl alcohol
- Both are polar
- Which substance moves with solvent?