| To design instruction using the Gagne-Briggs model of instructional design,
categorize learning outcomes and then organize instructional events for each kind
of learning outcome. There are nine instructional events, tailored to the kind of
outcome to be achieved that provide prescriptions in the form of activities and
interactions. These can be applied in any order. This model has been adapted to
web-based instruction. |
 |
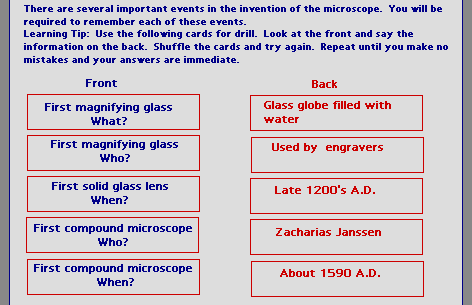
| David Merrill's Component Display Theory is based on the same
assumptions as Gagne's theory, that different classes of learning outcomes require
different procedures for teaching and assessment. CDT teaches individual concepts
or principles, classifies objectives on two dimensions and formats instruction to
provide student-directed learning. |
 |
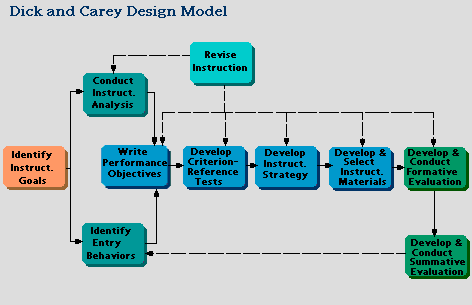
The Dick and Carey Design Model uses a systems approach for designing
instruction. One of the best known models, its approach to designing instruction is
similar to that of software engineering. The design model describes all the phases
of an iterative process that starts by identifying instructional goals and ends with
summative evaluation. This model is applicable across a range of context areas
(e.g., K-12 to business to government) and users (novice to expert). |
 |
| The Gerlach-Ely Design Model is a prescriptive model that is well suited to higher
education. It is meant for novice instructional designers who have knowledge and
expertise in a specific context. The model includes strategies for selecting and
including media within instruction. It also handles the allocation of resources. |
 |
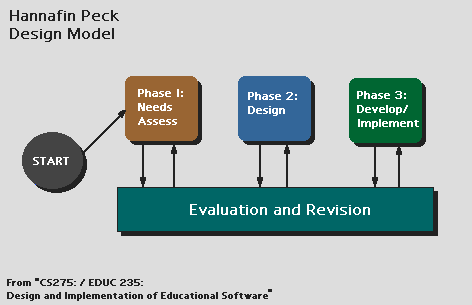
| The Hannafin /Peck Design Model is a three phase process. In the first phase, a
needs assessment is performed. This phase is followed by a design phase. In the
third phase, instruction is developed and implemented. In this model, all of the
phases involve a process of evaluation and revision. |
 |
The Jerrold Kemp Design Model takes a holistic approach to instructional design.
Virtually all factors in the learning environment are taken into consideration
including subject analysis, learner characteristics, learning objectives, teaching
activities, resources (computers, books, etc.), support services and evaluation. The
process is iterative and the design is subject to constant revision. This model is a
more advanced one to design by and the most comprehensive for web-based course
development. |
 |
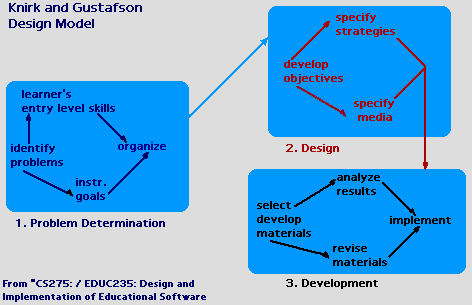
The Knirk and Gustafson Design Model is a three stage process which includes
problem determination, design and development. The problem determination stage
involves identifying the problem and setting instructional goals. The design stage
includes developing objectives and specifying strategies. Finally, in the development
stage, materials are developed. |
 |
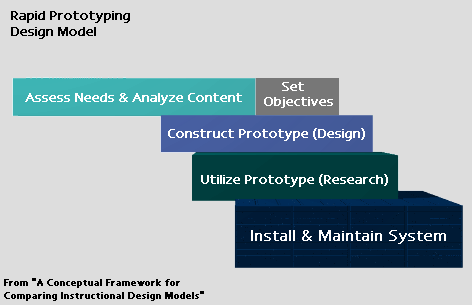
| Tripp and Bichelmeyer's Rapid Prototyping Design Model is a four level process that
is intended to create instruction for lessons as opposed to entire curricula. The
process stages include performing a needs analysis, constructing a prototype,
utilizing the prototype to perform research and installing the final system. This
model relies on expert instructional designers to utilize heuristics as well as their
past experience and intuition to guide the design. This is a very time consuming and
advanced model used mainly by those doing research. |
 |







